Extended Figure 9: Complex I deficient cells expressing LbNOX in the cytosol perform glutamine reductive carboxylation.
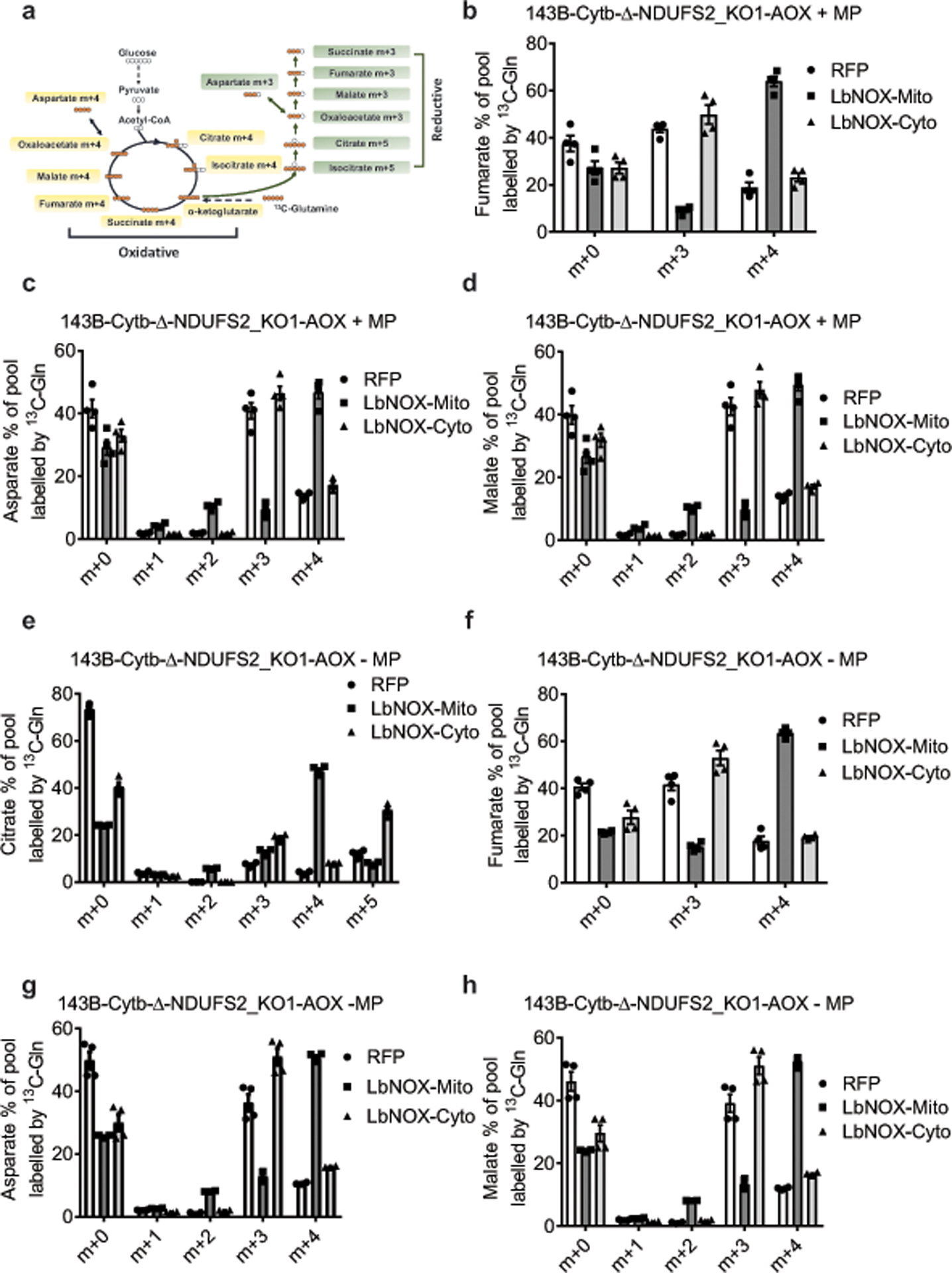
a, Schematic representation for oxidative and reductive glutamine metabolism. Metabolism of [U-13C]glutamine generates fully labeled α-ketoglutarate. Oxidation of α-ketoglutarate in the TCA cycle produces metabolites with four 13C-carbons (m+4), while reduction of α-ketoglutarate through the reductive carboxylation pathway produces citrate with five 13C-carbons (m+5). Further reductive metabolism of the m+5 citrate yields metabolites with three 13C-carbons (m+3). b-h, 143B-Cytb-Δ-NDUFS2_KO1-AOX-RFP, 143B-Cytb-Δ-NDUFS2_KO1-AOX-LbNOX-Mito, and 143B-Cytb-Δ-NDUFS2_KO1-AOX-LbNOX-Cyto cells were labeled for six hours with [U-13C]glutamine in the presence (b-d) or absence of methyl pyruvate (e-h), and percentage of labeled metabolite pools were examined. m+5 and m+3 pools result from glutamine flow through reductive metabolism. m+4 pools result from glutamine flow through oxidative metabolism. Data represent mean ± s.e.m. of 4 biologically independent experiments.
