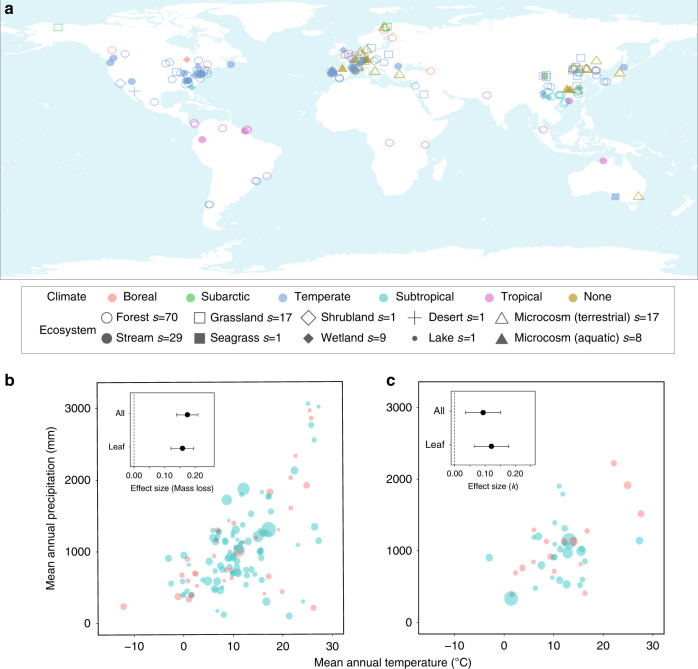
Fig. 1. Overview of the dataset.
a A map showing the geographical distributions of the studies for the diversity effect (species-mixing effect) on plant litter decomposition. Different shapes and colours of symbols represent different ecosystem types and climatic zones. The number of studies (s) is shown for each ecosystem type; note that some studies simultaneously conducted multiple experiments in different ecosystem types and climate regions. b, c Mean annual temperature and precipitation are shown for each of the studies that evaluated mass loss (131 studies) and/or the decomposition rate constant k (45 studies). Symbols represent each study, where the size of circles is proportional to the within-study mean effect size of Hedges’ d (based on mass loss and k as a measure of decomposition rate) and their colours if the mean is positive (blue) or negative (red). Small inset figures are the effect sizes (b mass loss; c the constant k), analyzed for all litter types and for leaf litter. Closed circles and error bars represent means and the 95% confidence intervals, respectively. A multilevel mixed effects meta-regression was used to account for a nested structure of the dataset. Vertical dotted lines are to indicate the effect size of zero.