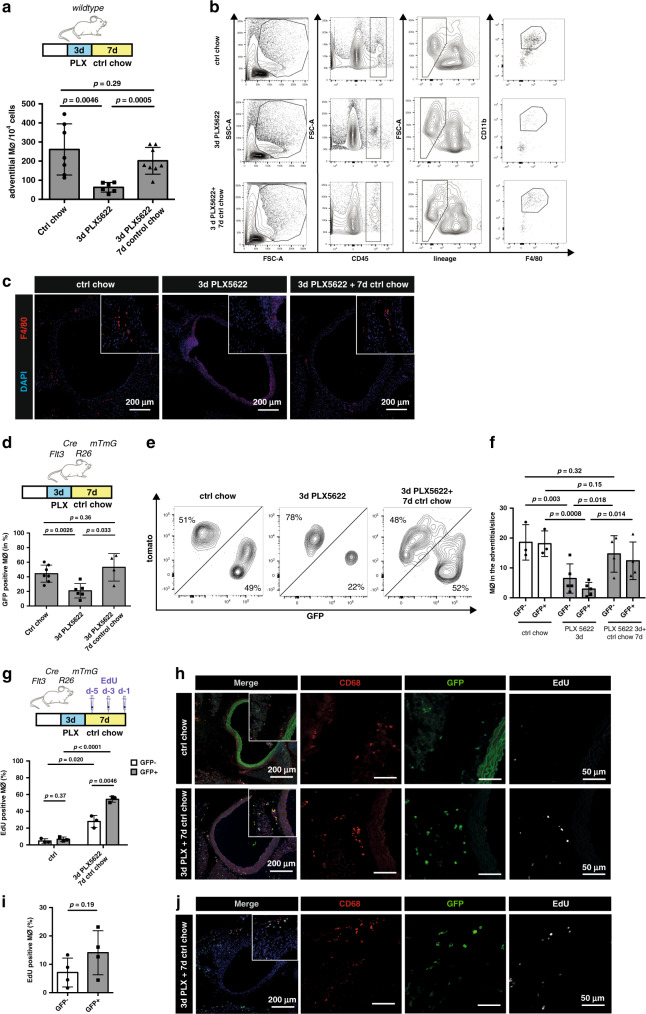
Fig. 4. BM-derived macrophages are more susceptible to Csf1r-inhibiton.
a–c CSF1R-inhibition in wildtype mice. a Schematic of macrophage depletion by CSF1R-inhibiton for 3 days (PLX5622 chow) followed by 7 days of control chow (recovery) and number of macrophages (Mϕ) in the adventitia of the respective treatment group (n = 7 for ctrl chow, n = 6 for 3 days of PLX5622; n = 8 for 3 days of PLX5622 followed by 7 days of control chow; two individual experiments for each condition). b Representative FACS analysis of all adventitial macrophages isolated from individual mice fed with either control chow (upper panel), 3 days of PLX5622 (middle panel) or 3 days of PLX followed by 7 days of control chow (lower panel). Adventitial macrophages were gated on CD45+, lineage− (CD11C, Ly6G, TER119, Siglec-F, TCR-ß, Nk1.1), CD11b+, F480hi. c Representative immunohistology of macrophages in the adventitia (n = 3, three independent experiments). d–j CSF1R-inhibition in Flt3CreRosa26mTmG mice. d Percentage of GFP+ macrophages in the adventitia (n = 7 for ctrl chow, n = 6 for 3 days of PLX5622; n = 4 for 3 days of PLX5622 followed by 7 days of control chow; two individual experiments for each condition). e Flow cytometry of tomato and GFP expression in adventitial macrophages. f Histological quantification of GFP + CD68 + macrophages (n = 3 for ctrl chow, n = 5 for 3 days of PLX5622; n = 4 for 3 days of PLX5622 followed by 7 days of control chow; 2 individual experiments for each condition). g, h Macrophage proliferation after depletion by PLX5622 in Flt3CreRosa26eYFP mice and injection of EdU i.p. either g 5, 3, and 1 days before euthanization (n = 3 for ctrl chow, n = 3 for 3 days of PLX5622 followed by 7 days of control chow; 1 individual experiments for each condition) or i only once 2 h before euthanization (to determine local proliferation; n = 4; 1 individual experiment). h, j Representative immunohistological images from aortas. Scale bar as depicted in images. Two-sided t-tests was performed and mean ± SD is shown.