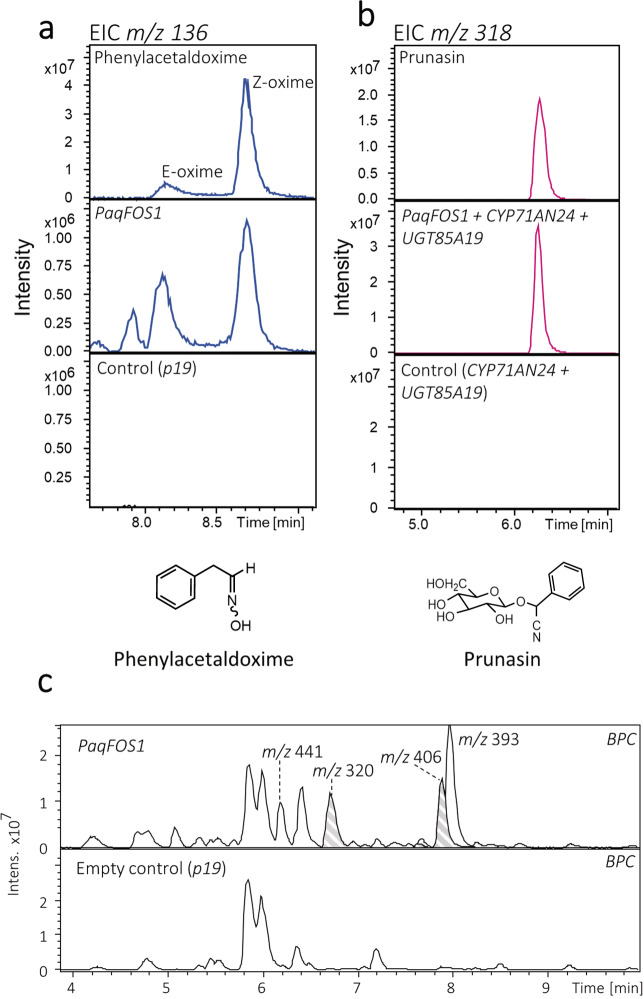
Fig. 4. LC–MS based metabolite analyses of Nicotiana benthamiana leaves transiently expressing PaqFOS1.
a Extracted ion chromatograms (EICs) for m/z 136 corresponding to the [M+H]+ adduct of authentic phenylacetaldoxime (upper panel), metabolite extracts from N. benthamiana leaves expressing PaqFOS1 (middle panel) and empty vector control (lower panel). b m/z 318 EICs corresponding to the [M+Na]+ adduct of an authentic prunasin standard (upper panel), metabolite extracts from N. benthamiana transiently expressing PaqFOS1 in combination with PdCYP71AN24 and PdUGT85A194,14 (middle panel) and the control expressing PdCYP71AN24 and PdUGT85A19 (lower panel). c Base peak chromatograms (BPCs) of the metabolite extracts from N. benthamiana leaves expressing PaqFOS1 using expression of p19 as an empty vector control show the formation of additional products: m/z 320 at 6.7 min corresponds to the [M+Na]+ adduct of glucosylated phenylacetaldoxime; m/z 406 at 7.6 and 7.9 min correspond to the [M+Na]+ adduct of a glycosylated, phenylacetaldoxime-malonic acid conjugate; and m/z 393.11 at 8.1 min correspond to the [M+Na]+ adduct of phenylethanol glucoside malonate ester2,10. For MS/MS of additional products, see Supplementary Fig. 3.