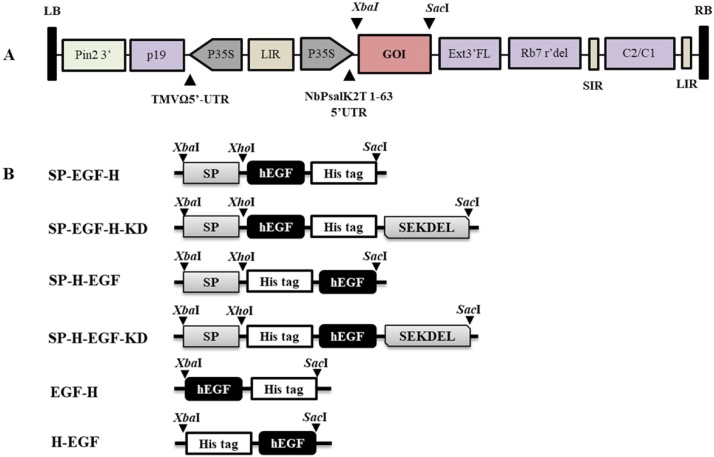
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of different plant expression vectors used in the present study: (A) Geminiviral vector was used for transient expression of hEGF in Nicotiana benthamiana. P35S: Cauliflower Mosaic Virus (CaMV) 35S promoter, TMVΩ 5′-UTR: 5′ untranslated region of tobacco mosaic virus Ω, hEGF gene: hEGF coding sequence, Ext3′ FL: 3′ full length of tobacco tabacum extention gene, SIR: short intergenic region of BeYDV genome, LIR: long intergenic region of BeYDV genome, C2/C1: Bean Yellow Dwarf virus (BeYDV) ORFs C1 and C2 which encode for replication initiation protein (Rep) and RepA, PNOS: nopaline synthase promoter, P19: P19 gene from Tomato Bushy Stunt Virus (TBSV), Nos3′: 3′ termini of the polyadenylated nos mRNA. (B) Six different hEGF gene constructs used in this study. SP: signal peptide at N-terminal, His tag: His tag residues at either N-terminus or C-terminus, hEGF: human epidermal growth factor, SEKDEL: C-terminal endoplasmic reticulum (ER) retention signal peptide. Arrowhead indicates the sites of restriction enzyme used for gene cloning (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article).