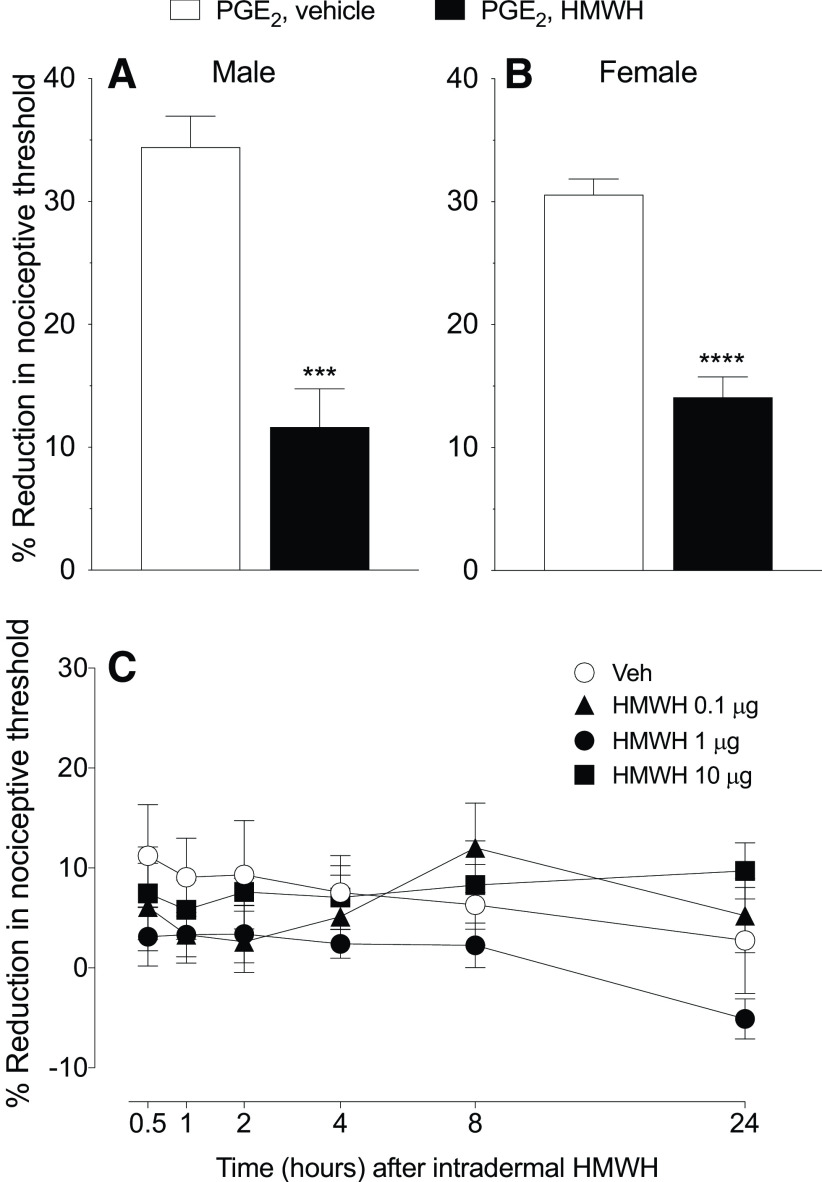
Figure 1.
HMWH attenuates PGE2 hyperalgesia but did not alone affect the nociceptive threshold. A, B, Male and female rats received PGE2 (100 ng/5 µl, intradermally) on the dorsum of the hindpaw followed 10 min later by HMWH (1 µg/5 µl) or vehicle (5 µl) injected at the same site. The mechanical nociceptive threshold was then measured 40 min after intradermal PGE2. Measurement of mechanical nociceptive threshold showed a significant attenuation of PGE2 hyperalgesia in rats treated with HMWH (A; t(10) = 5.676, ***p= 0.0002, when the vehicle-treated group was compared with the HMWH-treated group; unpaired Student's t test; B; t(10) = 7.860, ****p < 0.0001, when the vehicle-treated group was compared with the HMWH-treated group; unpaired Student's t test). n = 6 paws in each group. C, Male rats received an intradermal injection of one of three doses of HMWH [0.1 µg, black triangle; 1 µg, black circle; or 10 µg, black square; diluted in 5 µl of saline) or vehicle (5 µl, white circle). Mechanical nociceptive threshold was evaluated 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8, and 24 h after intradermal HMWH administration. The time course of the effect of HMWH on nociceptive threshold did not differ among the 0.1, 1, and 10 µg doses, and did not affect the nociceptive threshold itself. Repeated-measures two-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey's multiple-comparison test, revealed no significant interaction among the groups (interaction: F(15,100) = 1.168, p = 0.3088; time: F(5,100) = 1.241, p = 0.2959; dose: F(3,20) = 1.093, p = 0.3750). n = 6 paws in each group.