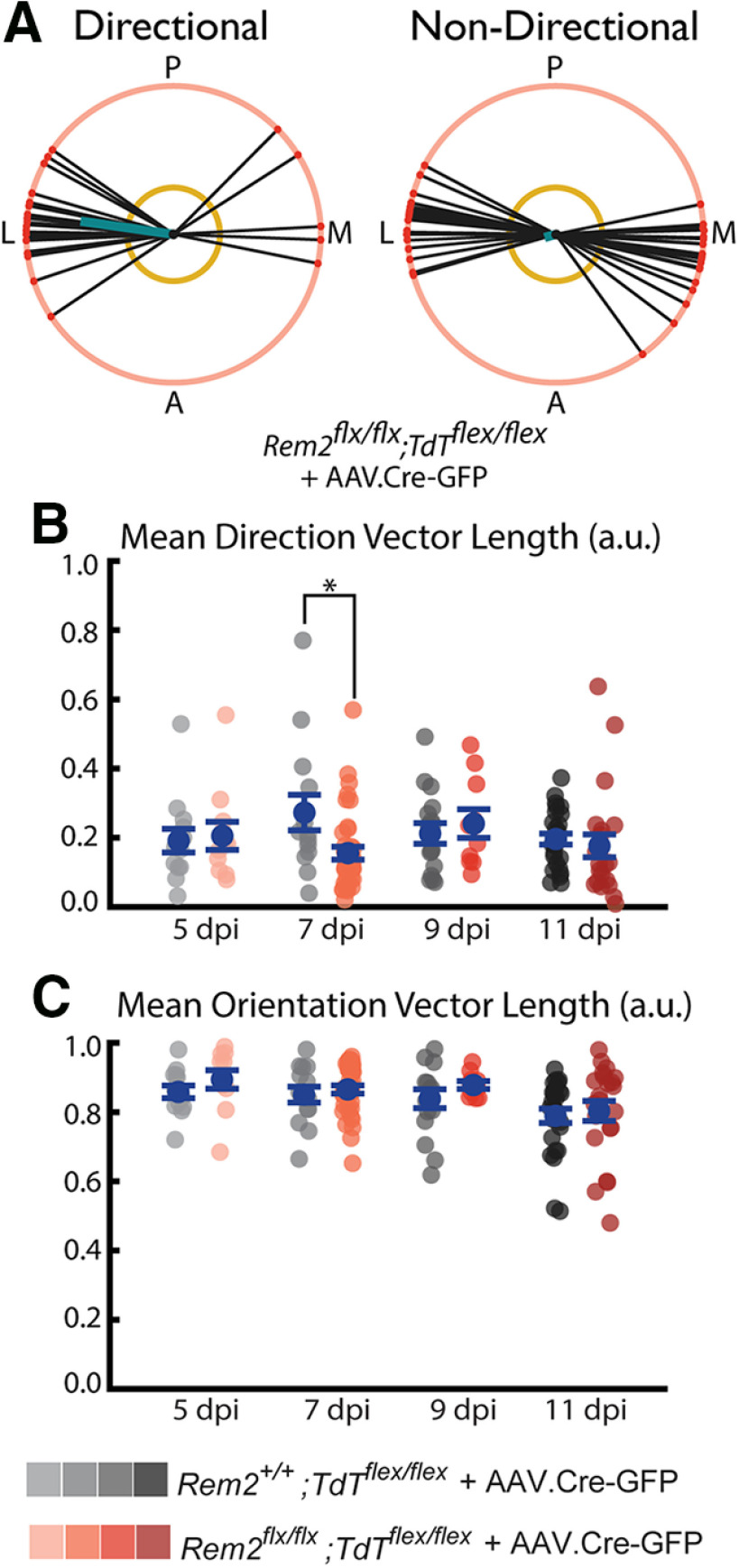
Figure 12.
Rem2 promotes basal dendrite tangential directionality. A, Example polar (left) and nonpolar (right) basal arbors sampled Rem2flx/flx;Tdtflex/flex + AAV.Cre-GFP mice in the tangential viewpoint. Each arbor is schematized as soma (center dot) and soma-to-tip vectors (lines with dots at tip) arranged on a unit circle. Thick teal line indicates the mean direction vector. Yellow circle represents length of mean direction vector required to declare the arbor directional by the Raleigh test. Posterior (P), anterior (A), medial (M), and lateral (L) are indicated around the diagrams. B, Length of the mean direction vector computed for Rem2+/+;Tdtflex/flex + AAV.Cre-GFP and Rem2flx/flx;Tdtflex/flex + AAV.Cre-GFP neurons sampled at 5, 7, 9, and 11 dpi. C, Length of the mean orientation vector computed for Rem2+/+;Tdtflex/flex + AAV.Cre-GFP and Rem2flx/flx;Tdtflex/flex + AAV.Cre-GFP neurons sampled at 5, 7, 9, and 11 dpi. Error bars indicate mean ± SEM. Blue dots indicate means. Gray/coral dots indicate single neurons. For all Rem2flx/flx;Tdtflex/flex + AAV.Cre-GFP measurements: 05 dpi, N = 11 cells, 4 mice; 07 dpi, N = 38 cells, 7 mice; 09 dpi, N = 10 cells, 4 mice; 11 dpi, N = 22 cells, 4 mice. For all Rem2+/+;Tdtflex/flex + AAV.Cre-GFP measurements: 05 dpi, N = 13 cells, 5 mice; 07 dpi, N = 14 cells, 5 mice; 09 dpi, N = 17 cells, 4 mice; 11 dpi, N = 27 cells, 6 mice. *p < 0.05 (Wilcoxon rank-sum test).