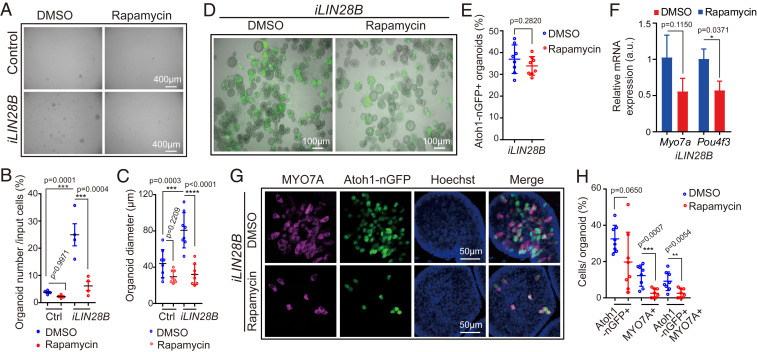
Fig. 7.
Inhibition of mTOR signaling attenuates LIN28B-induced organoid growth and hair cell formation. Cochlear organoid cultures were established from stage P5 Atoh1-nGFP;iLIN28B transgenic mice and Atoh1-nGFP transgenic control littermates and maintained as outlined in Fig. 2A. (A–C) Rapamycin attenuates LIN28B’s positive effect on cell growth in organoid culture. Rapamycin (4 ng/mL) or vehicle control (DMSO) was added at plating and replenished every other day. (A) BF images of control and LIN28B overexpressing (iLIN28B) organoids after expansion in the presence of DMSO or rapamycin for 7 d. (B) Organoid-forming efficiency in A (n = 4, two independent experiments). (C) Organoid diameters in A (n = 8, three independent experiments). (D–H) Rapamycin attenuates LIN28B’s positive effect on hair cell formation in organoid culture. Rapamycin (4 ng/mL) or DMSO was present during the final phase of expansion (10 to 13 d) and during the 5 d of differentiation. (D) Merged BF and green fluorescent images (Atoh1-nGFP) of LIN28B overexpressing organoid cultures treated with DMSO or rapamycin. (E) Percentage of Atoh1-nGFP+ organoids in D (n = 8, two independent experiments). (F) qRT-PCR analyzing Myo7a and Pou4f3 mRNA expression in LIN28B overexpressing organoids treated with rapamycin (red bar) or DMSO (blue bar) (mean ± SD, n = 2, from one representative experiment, two independent experiments). (G) Confocal images of LIN28B overexpressing organoids cultured in the presence of rapamycin or DMSO. Newly formed hair cells are identified by their coexpression of Atoh1-nGFP (green) and MYO7A (magenta). Nuclei were counterstained with Hoechst (blue). (H) Percentage of GFP+ (Atoh1-nGFP), MYO7A+, and GFP+ MYO7A+ hair cells per organoid in G (n = 8, two independent experiments). Graphs in B, C, E, and H show individual data points and the mean ± SD. The individual data points in C, E, and H represent average value per animal. n = animals analyzed per group. Two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s correction was used to calculate P values in B and C. Otherwise, P values were calculated using two-tailed, unpaired Student’s t tests.