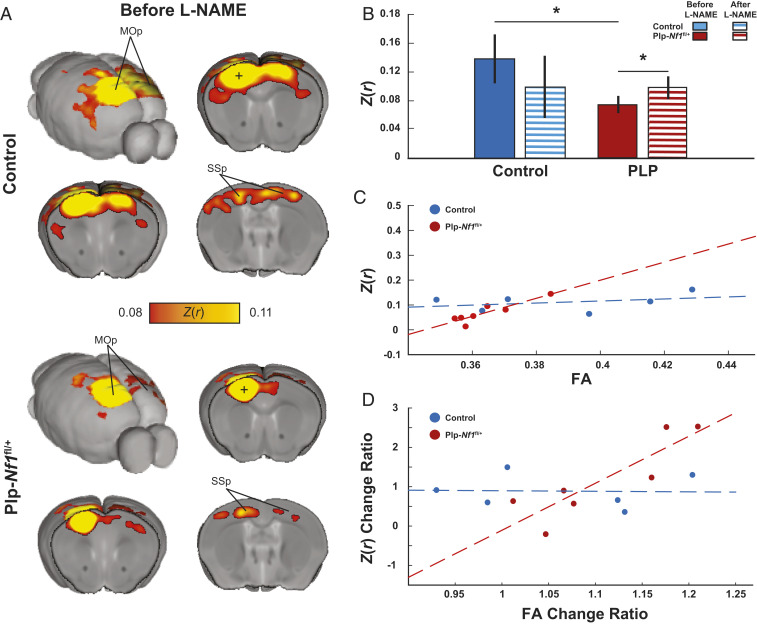
Fig. 4.
Reduced brain-wide connectivity in the motor network is rescued by L-NAME treatment. (A) Group average correlation maps demonstrate reduced interhemispheric connectivity between control (Top) and Plp-Nf1fl/+ (Bottom) mice. Z(r), Fisher’s Z- transformed r; MOp, primary motor cortex; SSp, primary somatosensory cortex. (B) Correlation of seed-to-seed analysis in the primary motor cortex (denoted as a plus sign in the maps shown in A), plotted for each group before and after L-NAME treatment, demonstrating reduced connectivity between control and Plp-Nf1fl/+ that is rescued by inhibition of NOS. (C) FA in the corpus callosum is plotted as a function of interhemispheric functional connectivity of the motor cortex. The dashed lines represent linear fit for control (blue) and Plp-Nf1fl/+ (red). (D) Structural and functional change due to treatment are plotted. FA change ratio defined as and functional connectivity Z(r) change ratio defined as are plotted. Dashed lines represent linear fit for control and Plp-Nf1fl/+.