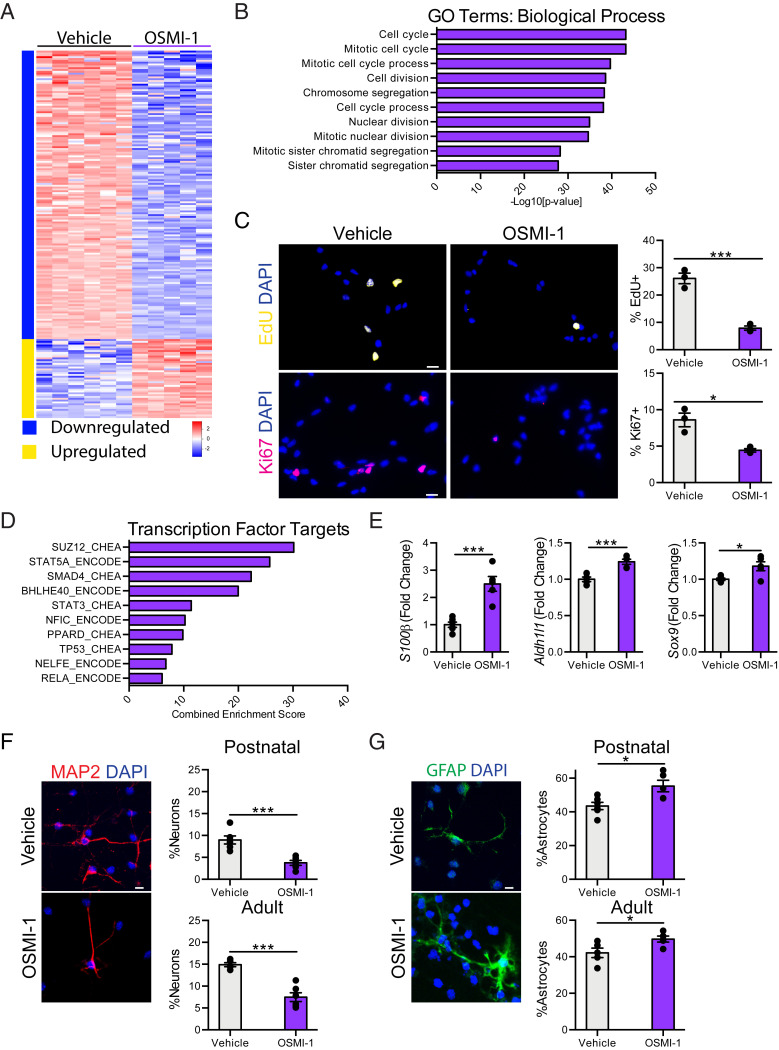
Fig. 2.
Decreased NSC O-GlcNAcylation promotes a neuron to glia fate switch in vitro. (A) Heatmap of significantly differentially expressed genes with fold-change > 2 and P < 0.05 in primary hippocampal NSCs following 24-h 12.5 µM OSMI-1 treatment compared to vehicle control in vitro. (B) Biological process GO terms associated with genes down-regulated following OSMI-1 treatment. (C) Representative field and quantification of primary mouse hippocampal NSCs following 24 h of vehicle (Left) or OSMI (Right) treatment, labeled with DAPI and an 8-h EdU-pulse (Upper), or DAPI and anti-Ki67 (Lower) (n = 3 per group). (Scale bars, 10 µm.) (D) Quantification of enriched transcription factor targets as identified by ChEA or ENCODE based on up-regulated genes after 24-h OSMI-1 treatment compared to vehicle control. (E) Fold-change expression (FPKM) of astrocyte-associated genes: S100β, Aldh1l1, and Sox9 in primary hippocampal NSCs following OSMI-1 treatment in vitro (n = 5 to 6 per group). (F) Differentiation was induced in vehicle or OSMI-1 treated primary postnatal (P1) and adult (2-mo-old) hippocampal NSCs by withdrawing growth factors 7 d prior to fixation. Cells were labeled with DAPI and anti-MAP2. MAP2+ neurons were quantified as a percentage of total DAPI+ cells (n = 6 replicates per group). (Scale bar, 10 µm.) (G) Primary postnatal and adult hippocampal NSCs were treated as in F. Cells were labeled with DAPI and anti-GFAP. GFAP+ astrocytes were quantified as a percentage of total DAPI+ cells (n = 6 per group). (Scale bar, 10 µm.) Data are represented as mean ± SEM; *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001; t test.