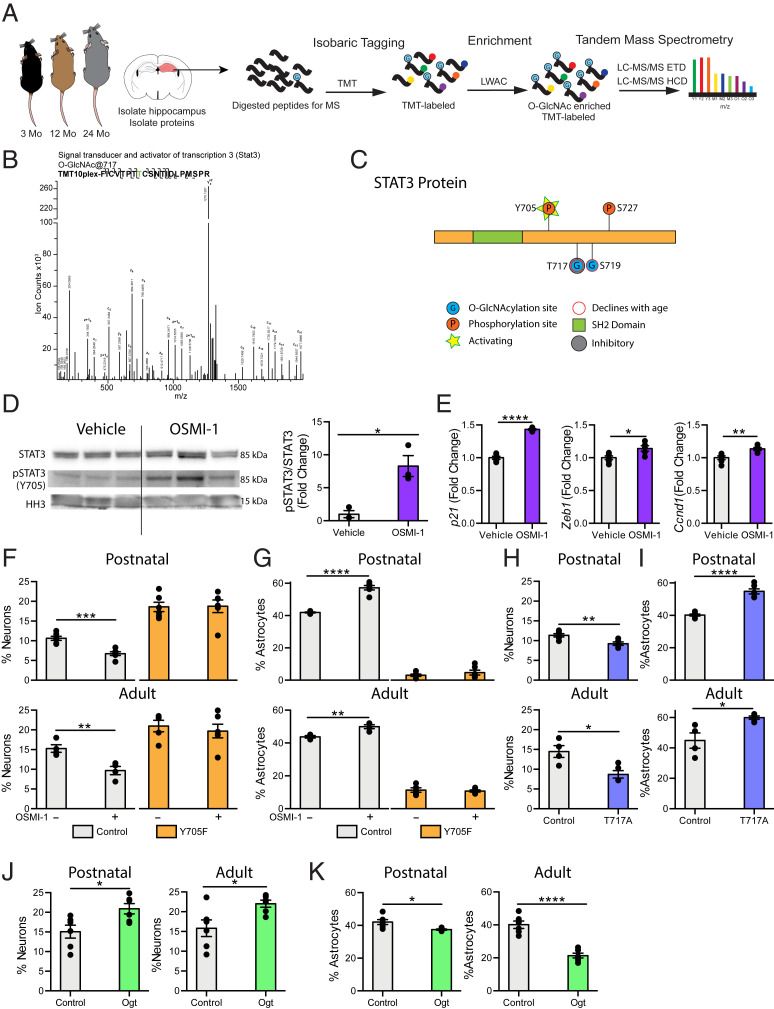
Fig. 4.
STAT3 O-GlcNAcylation at T717 is reduced in the aging hippocampus and mimicking this decline in NSC promotes a gliogenic fate switch. (A) Schematic of proteomic workflow. The hippocampus was isolated from 3-, 12-, or 24-mo-old mice. Hippocampi were pooled to obtain sufficient protein (n = 5 animals per pool). Proteins were isolated from tissue and digested with trypsin before undergoing isobaric tagging. Tagged peptides were enriched for O-GlcNAcylation with LWAC and analyzed via electron transfer dissociation mass spectrometry (ETD-MS). (B) Representative spectra of hippocampal STAT3 O-GlcNAcylation at T717. (C) Diagram of O-GlcNAc sites detected by mass spectrometry in A (T717, S719), and previously identified phosphorylation sites (Y705, S727) on STAT3. (D) STAT3 phosphorylation at Y705 and STAT3 expression in primary hippocampal NSCs following 24-h vehicle or OSMI-1 treatment (n = 3 per group). (E) Expression of STAT3 target genes in primary hippocampal NSCs treated as in D was evaluated using RNA-sequencing. (F) Primary hippocampal postnatal and adult NSCs were infected with a lentiviral construct expressing a nonphosphorylatable STAT3 (Y705F) or wild-type STAT3 (Control). Differentiation was induced in vehicle or OSMI-1 treated NSCs by withdrawing growth factors 7 d prior to fixation. Cells were labeled with DAPI and anti-MAP2. MAP2+ neurons were quantified as a percentage of total DAPI+ cells (n = 6 replicates per group). (G) Primary postnatal and adult hippocampal NSCs were infected, treated, and differentiated as in F. Cells were labeled with DAPI and anti-GFAP. GFAP+ astrocytes were quantified as a percentage of total DAPI+ cells (n = 6 replicates per group). (H) Primary postnatal and adult hippocampal NSCs were infected with a lentiviral construct expressing an O-GlcNAcylation–deficient STAT3 (T717A) or wild-type STAT3 (Control). Differentiation was induced by withdrawing growth factors 7 d prior to fixation. Cells were labeled with DAPI and anti-MAP2. MAP2+ neurons were quantified as a percentage of total DAPI+ cells (n = 6 replicates per group). (I) Primary postnatal and adult hippocampal NSCs were infected, treated, and differentiated as in H. Cells were labeled with DAPI and anti-GFAP. GFAP+ astrocytes were quantified as a percentage of total DAPI+ cells (n = 6 replicates per group). (J) Primary postnatal and adult hippocampal NSCs were infected with a lentiviral construct expressing Ogt or GFP under the Nestin promoter. Differentiation was by induced withdrawing growth factors 7 d prior to fixation. Cells were labeled with DAPI and anti-MAP2. MAP2+ neurons were quantified as a percentage of total DAPI+ cells (n = 6 replicates per group). (K) Primary postnatal and adult hippocampal NSCs were infected, treated, and differentiated as in J. Cells were labeled with DAPI and anti-GFAP. GFAP+ astrocytes were quantified as a percentage of total DAPI+ cells (n = 6 replicates per group). Data are represented as mean ± SEM; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001; t test.