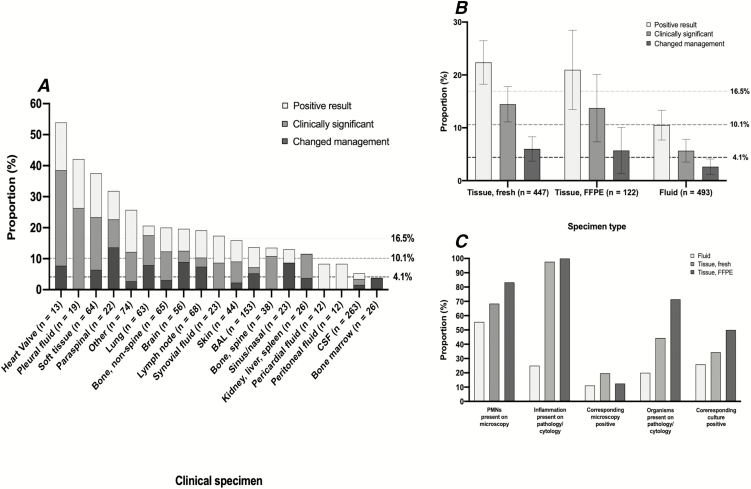
Figure 1.
A, The clinical utility of universal broad-range polymerase chain reaction amplicon sequencing (uPCR) by clinical specimen type. The bars are overlapping and the 3 horizontal, dashed lines represent the overall proportion of all samples with corresponding positive uPCR results (16.5%), positive uPCR results that were clinically significant (10.1%), and positive uPCR results that changed clinical management (4.1%). B, The clinical utility of uPCR by clinical sample type: fresh tissue, formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue, or fluid sample. C, The proportion of clinical samples, stratified by sample type, that have a corresponding positive microbiological or pathology result. Abbreviations: BAL, bronchoalveolar lavage; CSF, cerebrospinalfluid; FFPE, formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded; PMN, polymorphonuclear neutrophil.