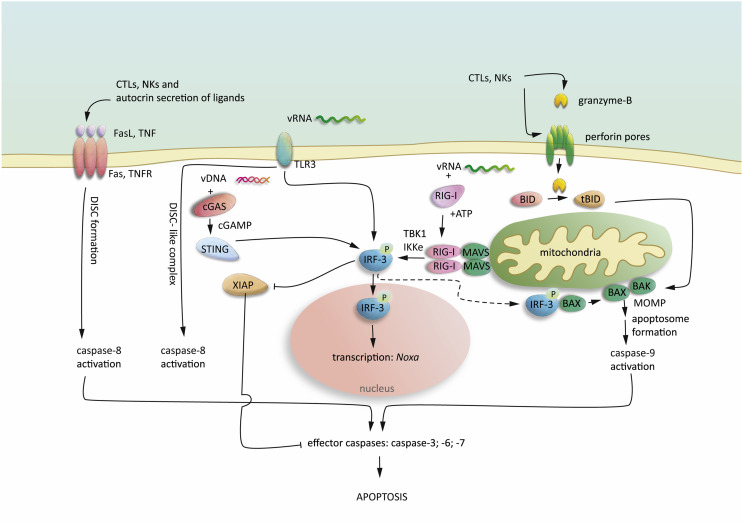
Fig. 1.
Apoptosis signalling in virus infection.
Virus infection leads to immune-stimulation and activation of CTLs and NK cells. CTLs and NK cells release cytotoxic perforin and granzyme-B. Granzyme-B enters the cells via the transmembrane perforin pores and results in BID cleavage, leading to BAX and BAK activation and MOMP-driven apoptosome formation and caspase-9 activation. Stimulation of death receptors (Fas and TNFR) initiate caspase-8 activation by the formation of death inducing signalling complex (DISC). Intracellular viral RNA (vRNA) is recognized by RIG-I, leading to ATP-dependent conformational changes and recruitment of MAVS oligomers, which in turn lead to the recruitment of TBK-1 and IKKε, resulting in phosphorylation of IRF-3. Extracellular vRNA is detected by TLR3 leading to IRF-3 activation. vDNA in the cytosol is recognized by cGAS, resulting in cGAMP production and activation of STING, which in turn activates IRF-3. Once IRF-3 is activated can translocate into the nucleus and induce transcriptional pathways leading to anti-viral response and apoptosis. Moreover, RIG-I activation promotes XIAP degradation and activation of pro-apoptotic BAX.