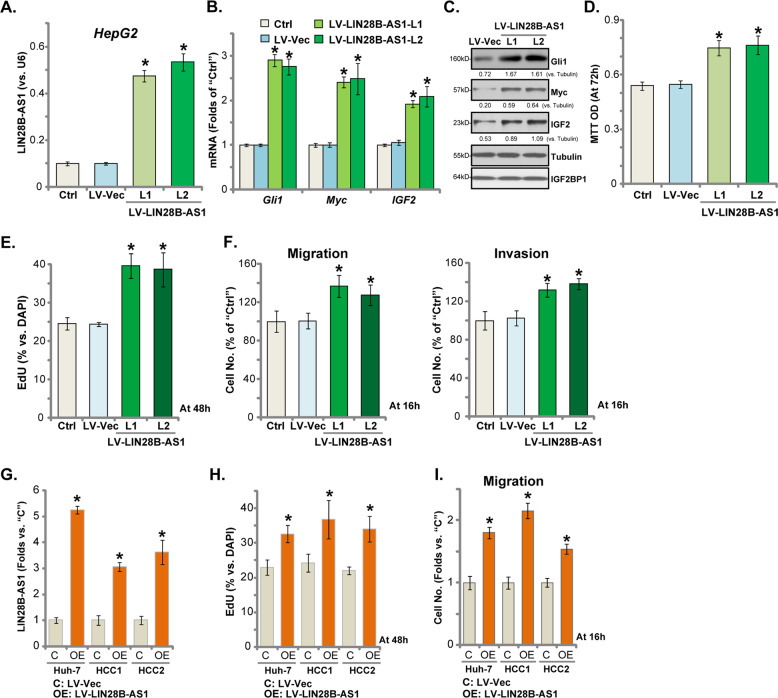
Fig. 4. Ectopic LIN28B-AS1 overexpression promotes human HCC cell progression in vitro.
Total RNA was extracted from the stable HepG2 cells with the lentiviral pre-LIN28B-AS1 expression construct (“LV-LIN28B-AS1”, two lines, “L1/L2”) or empty vector (“LV-Vec”), LIN28B-AS1 a as well as Gli1, Myc, and IGF2 mRNAs b were tested; Listed proteins were tested by Western blotting c. Cells were further cultured for applied time periods, cell survival, and proliferation were tested by MTT d and EdU staining e assays, respectively; Cell migration and invasion were tested by “Transwell” and “Matrigel Transwell” assays, with results quantified f, respectively. Huh7 cells and primary HCC cells (“HCC1/2”) were transduced with LV-LIN28B-AS1 or LV-Vec, and stable cells established with puromycin selection. Expression of LIN28B-AS1 was tested g, with cell proliferation and migration examined by EdU incorporation h and “Transwell” assays i, and results were quantified. Listed proteins were quantified and normalized c. Data were presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD, n = 5). *p < 0.05 vs. “LV-Vec” cells. The experiments were repeated three times, and similar results were obtained.