Figure 1.
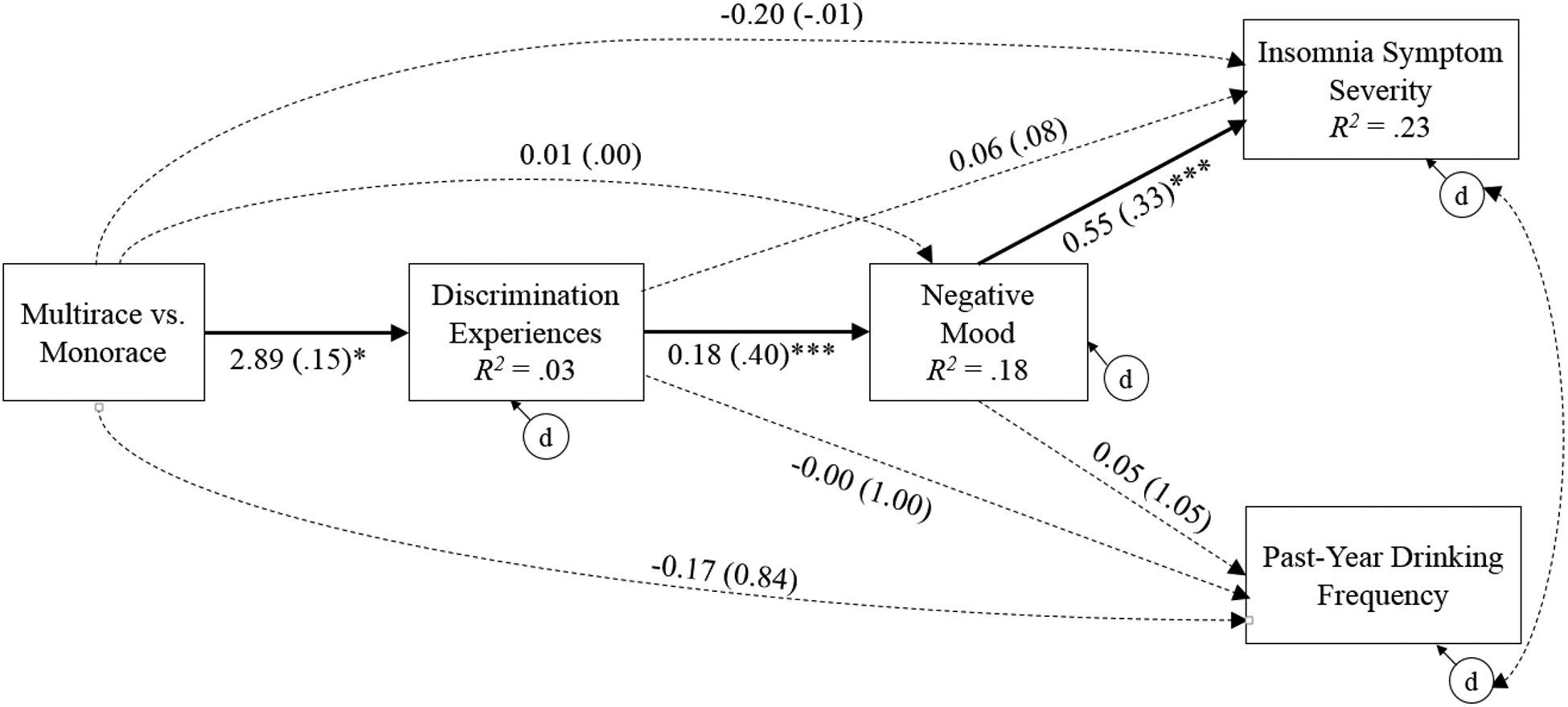
N = 414. Results from a fully saturated path model testing the serial indirect pathway for multiracial (vs. monoracial) adolescents after controlling for age, sex, Hispanic/Latinx ethnicity, and eligibility for free/reduced-price lunch; covariate pathways are not shown for simplicity. Unstandardized (and standardized) coefficients for paths leading to continuous variables (discrimination experiences, negative mood, and insomnia symptom severity) and unstandardized coefficients (and incidence rate ratios; IRR) for paths leading to a count variable (past-year alcohol frequency; negative binomial dispersion parameter=0.00, p=.75) are shown. Dotted paths indicate non-significant paths. The serial indirect pathway was significant for insomnia symptom severity (b=0.28, SE =.14, p=.05, 95% bootstrapped CI [0.04, 0.47]), but not past-year drinking frequency (b=0.02, SE =.02, p=.30, 95% bootstrapped CI [−0.00, 0.07]). d=disturbance/residual. *p<.05; ***p<.001.
