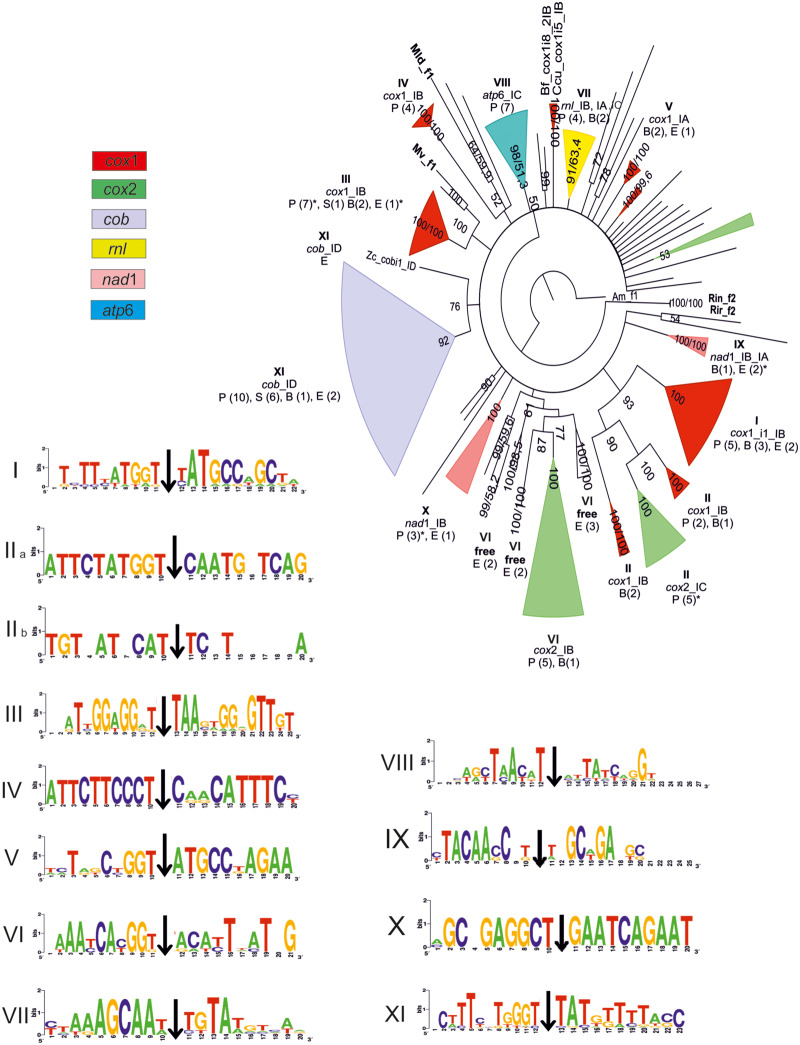
Fig. 4.
Phylogenetic tree of the GIY-YIG amino acid matrix as produced by employing the BI method. Major clades are shown as filled colored triangles and their different colors indicate different mt genes carrying the introns which hosted the GIYs examined. In detail: mt genes cox1, cox2, cob, rnl, nad1, and atp6 are presented in red, green, gray, yellow, pink, and blue, respectively. Roman numbers show the major clades analyzed in the text and their target insertion sequence of their introns shown additionally as logos. Numbers at the nodes of the tree present the posterior probability (first or unique number) and the NJ-bootstrap (second number, when NJ topology is identical with the respective of the BI tree). Species names are omitted unless they are basal to a cluster discussed in the text (they are provided in supplementary fig. S1, Supplementary Material online). Single letters represent taxonomical units as follows: P, Pezizomycotina; S, Saccharomycetes; B, Basidiomycota; and E, EDF. The parentheses following the single letters represent the number of species found in the examined clusters. Asterisks indicate single alternative topology (either intron subtype or gene or both) among its cluster (see details in supplementary fig. S1, Supplementary Material online).