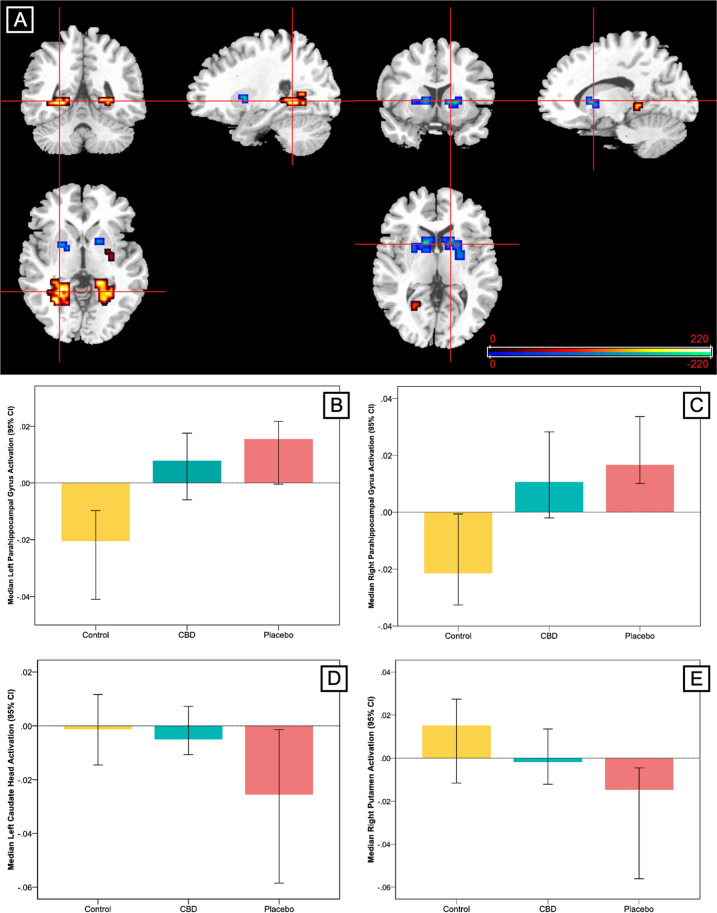
Fig. 2. Effect of cannabidiol (CBD) on brain activation compared with placebo in participants at clinical high risk of psychosis (CHR) and healthy control participants.
a Clusters where activation differed across the three groups in a linear relationship during fear processing. In the parahippocampal region (red/yellow), activation was greatest in the group of clinical high risk participants receiving placebo, lowest in healthy controls and intermediate in the CBD group. In the striatum (blue/green), activation was greatest in healthy controls, lowest in participants at clinical high risk receiving placebo and intermediate in participants at clinical high risk receiving CBD. The right side of the brain is shown on the right of the images. b–e Median activation in each group in b the left parahippocampal gyrus, c the right parahippocampal gyrus, d left caudate head and e right putamen during fear processing in arbitrary units as indexed using the median sum of squares ratio. The sum of squares ratio statistic refers to the ratio of the sum of squares of deviations from the mean image intensity due to the model (over the whole time series) to the sum of squares of deviations due to the residuals.