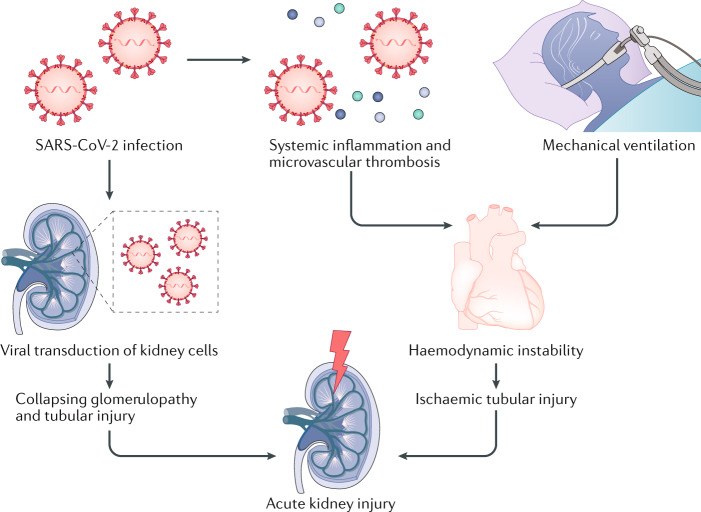
Fig. 1. Potential mechanisms of AKI in COVID-19.
SARS-CoV-2 may transduce podocytes, possibly leading to collapsing glomerulopathy. Alternatively, tubular epithelial transduction could lead to tubular injury and acute kidney injury (AKI). SARS-CoV-2 infection of lung parenchyma leads to systemic inflammation and microvascular thrombosis, contributing to haemodynamic instability. Peri-intubation hypotension may worsen kidney perfusion, leading to ischaemic tubular injury and AKI.