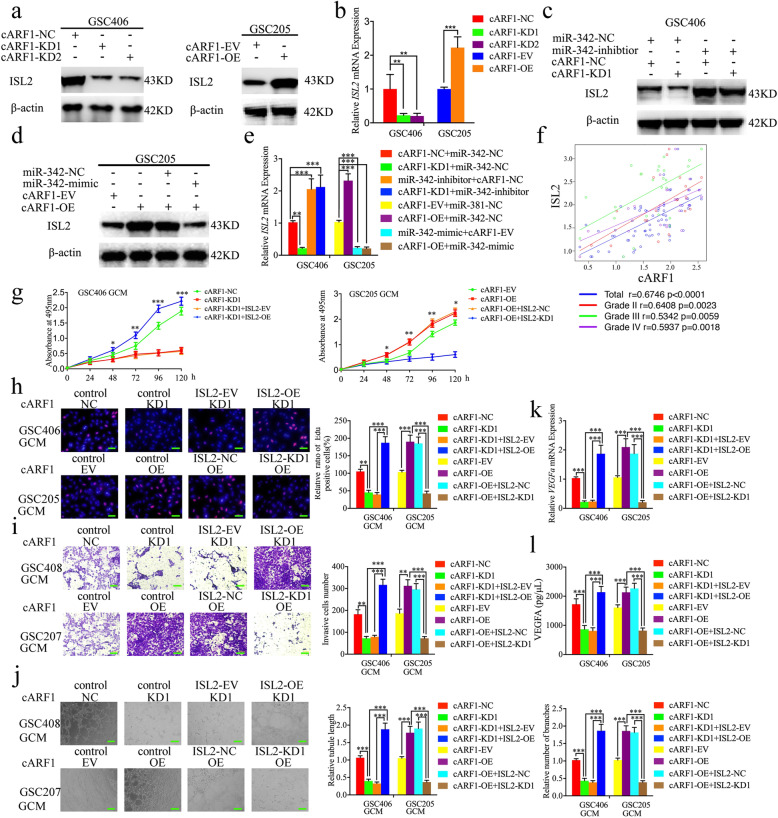
Fig. 5.
The cARF1 promoted the proliferation, invasion, and angiogenesis of hBMECs with GCM by upregulating ISL2 expression. a, b The western blot (a) and qPCR (b) showed the expression of ISL2 in GSCs after cARF1 overexpression (left) or knockdown (right). c The decreased expression of ISL2 in GSC406 induced by cARF1 knockdown was reversed by miR-342–3p inhibitor treatment, as determined by western blotting. d The increased expression of ISL2 in GSC205 induced by cARF1 overexpression was reversed by miR-342–3p mimic treatment, as determined by western blotting. e The effect of both cARF1 and miR-342–3p on the mRNA expression of ISL2 in GSCs was detected by qPCR. f The qPCR showed the mRNA expression correlation between ISL2 and cARF1 in 70 cases of glioma patients. g MTS assays showed that hBMEC cell viability with cARF1 knockdown or overexpression GCM were reversed by ISL2 overexpression or knockdown, respectively. h The EDU assay showed the proliferation of hBMECs with cARF1 knockdown or overexpression of GCM were reversed by ISL2 overexpression or knockdown, respectively. Scale bar = 50 μm. i A representative Transwell assay showed the invasion of hBMECs with cARF1 knockdown or overexpression of GCM were reversed by ISL2 overexpression or knockdown, respectively. Scale bar = 100 μm. j A representative tube formation assay showed that the tubulogenesis of hBMECs with cARF1 knockdown or overexpression of GCM were reversed by ISL2 overexpression or knockdown, respectively. Scale bar = 100 μm. k, l The qPCR (k) and ELISA assay (l) indicated that the mRNA expression and secretion of VEGFA in GSCs after cARF1 knockdown or overexpression were reversed by ISL2 overexpression or knockdown, respectively. EV: empty vector, OE: overexpression, NC: negative control, KD: knockdown. All data are expressed as the mean ± SD (three independent experiments). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001