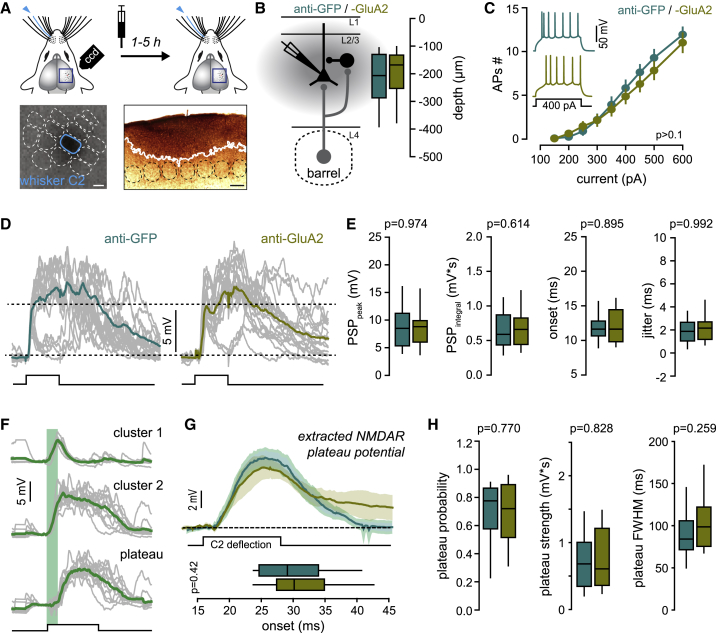
Figure 3.
Cross-linking GluA2 Does Not Affect Short- and Long-Latency Whisker Subthreshold Responses
(A) Left: IgG is stereotaxically injected in FWE mice, in the superficial layers of the PW column identified by intrinsic optical imaging. Right: DAB immunostaining. White line, maximum spread of IgG. Scale bars, 100 μm.
(B) Schematic of the excitatory/inhibitory feed-forward circuit in a barrel-related column. L2/3 pyramidal neurons are recorded in the PW barrel-related column after IgG injection. Depth of recorded cells is indicated.
(C) Average (± SEM) number of action potentials (APs) triggered by incremental current injections. Insert: example of spiking pattern in anti-GFP- and anti-GluA2-injected mice upon 400-pA current injection.
(D) Single-cell example of PW-evoked PSP. Individual trials are represented with gray lines. Square pulse line, whisker deflections (100 ms).
(E) Median (± interquartile range) PSP peak amplitude, integral, onset, and onset jitter (anti-GFP, n = 34 cells; anti-GluA2, n = 31 cells).
(F) Example of NMDAR plateau strength extraction.
(G) Top: grand average of PW-evoked extracted plateau potential (all recorded cells averaged ± SEM). Black square pulse line, C2 whisker deflection (100 ms). Bottom: median (± interquartile range) onset of plateau potentials.
(H) Median (± interquartile range) plateau probability, strength (mV∗s), and full width at half maximum (FWHM, in milliseconds) in anti-GFP-injected (n = 26 cells) and anti-GluA2-injected (n = 24 cells) mice.