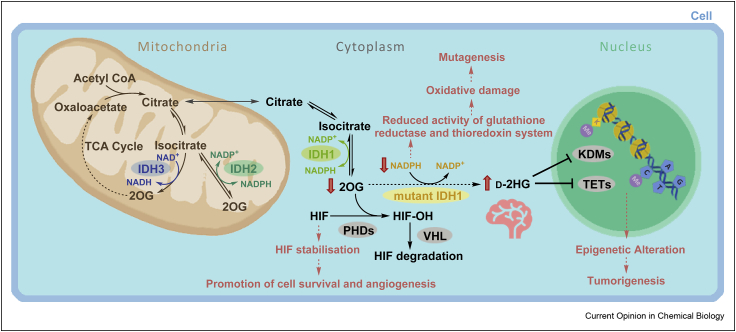
Figure 2.
Roles of wt IDH1/2/3 and some of the potential multiple effects of IDH mutation in cells (exemplified for IDH1). Different subcellular localisations (IDH1: cytoplasm; IDH2/3: mitochondria) and cosubstrate usage (IDH1/2: NADP+; IDH3: NAD+) distinguish the 3 human IDHs. The effects of IDH1 variants, including promotion of tumorigenesis, are proposed to manifest because of metabolic changes including d-2HG accumulation, depletion of NADPH and/or reduced 2OG. Changes in d-2HG/2OG levels are proposed to inhibit 2OG oxygenases involved in regulation of expression, for example, PHD, JmjC KDM, or TET enzymes. 2OG, 2-oxoglutarate; d-2HG, d-2-hydroxyglutarate; IDH, isocitrate dehydrogenase; HIF, hypoxia-inducible factor; HIF–OH, hydroxylated HIF; PHD, HIF prolyl hydroxylase domain enzyme; KDM, histone lysine demethylase; NADP+, oxidised nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; NADPH, reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; TCA, tricarboxylic acid; TET, ten-eleven translocation oxygenase; VHL, Von Hippel-Lindau; wt, wild-type.