Figure 6.
Xenotransplantation Indicates That XRC Treatment after Gene Editing Leads to Efficient HDR in Long-Term Engrafting HSCs
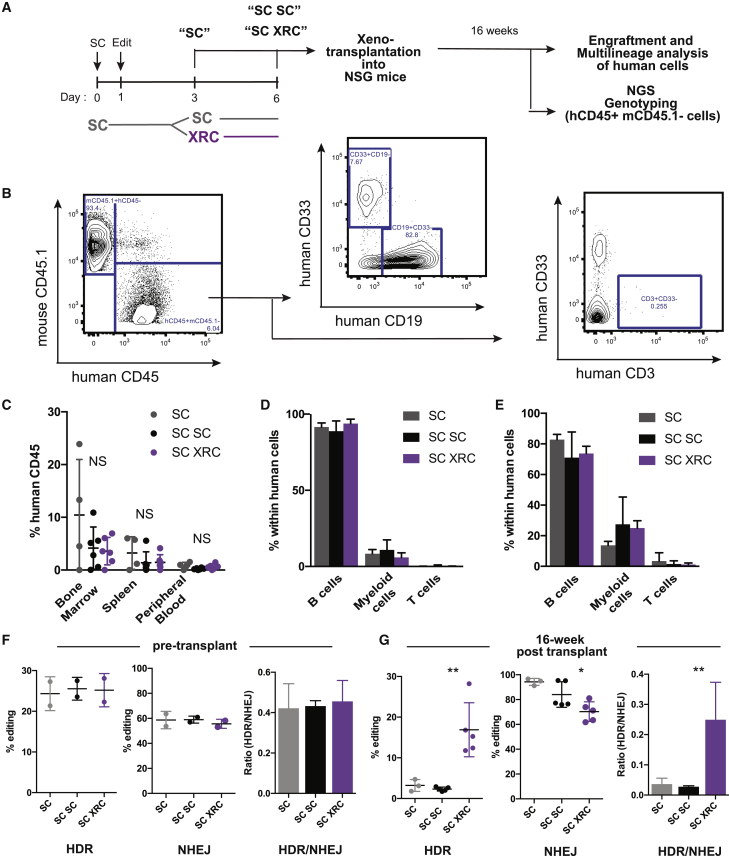
(A) Schematic of the workflow for xenotransplantation. CD34+ HSPCs are placed in SC culture for 1 day before editing and cycle for 2 additional days in SC culture, and then quiescence is induced with XRC for 3 days before xenotransplantation into NSG mice. Sixteen weeks post-transplant, bone marrow is collected for engraftment analysis, multilineage analysis, and NGS genotyping; spleen is collected for engraftment analysis; and peripheral blood is collected for engraftment and multilineage analysis.
(B) Gating strategy for measuring human cell engraftment and multilineage differentiation.
(C) Human cell engraftment (human CD45/mouse CD45.1) 16 weeks after transplant in the bone marrow, spleen, and peripheral blood of NSG mice. Data from individual mice and mean ± SD shown. n = 4 or 6. NS, not significantly different by unpaired t test.
(D and E) Percentage of indicated lineages (B cells [CD19], myeloid cells [CD33], and T cells [CD3]) within the human cell graft in the bone marrow (D) and peripheral blood (E) of NSG mice. Data from individual mice and mean ± SD shown. n = 4 or 6.
(F and G) Editing outcomes in CD34+ HSPCs before transplanting into NSG mice (F) and in hCD45+mCD45.1− cells from the bone marrow of NSG mice 16 weeks after transplant (G) (SC, 3 days in SC media; SC SC, 6 days in SC media; SC XRC, 3 days in SC media and 3 additional days in XRC before transplant). Data from individual mice and mean ± SD shown. n = 3 or 5 for each condition (mice with engraftment < 2% were excluded from this analysis due to insufficient cell number for amplicon sequencing). ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01 by unpaired t test.
Representative data from experiments performed with two different mPB donors and n = 4–6 biological replicates per donor.