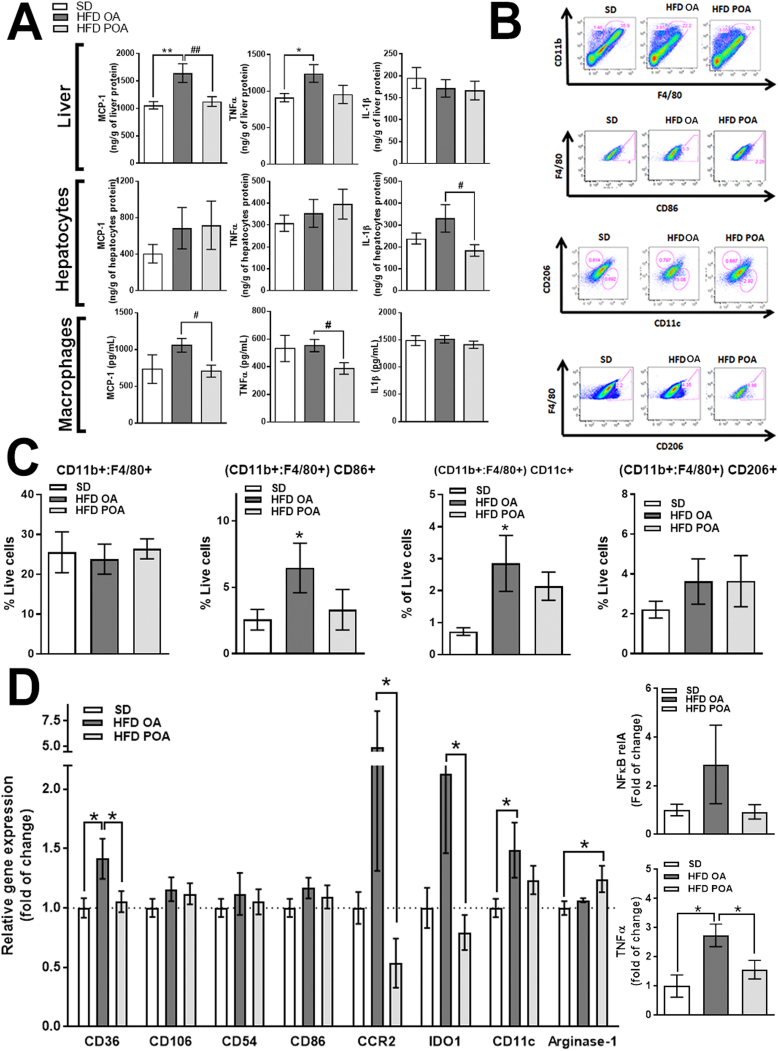
Fig. 3.
Palmitoleic acid promotes anti-inflammatory effects in liver of HFD-fed mice by modulation of the liver macrophage population. (A) Monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP)-1, interleukin (IL)-1β and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α levels in liver, hepatocytes and liver macrophages (LM) (n = 11–15); (B) flow cytometry gate strategy (representative of n = 4–5); (C) % of F4/80, CD11c, CD86 and CD206 positive LM (n = 4–5), (D) relative mRNA expression of inflammation-related genes in LM (n = 5–7). Wild-type (WT) mice fed with a standard diet (SD) or high-fat diet treated with oleic acid (HFD OA) or palmitoleic acid (HFD POA). Ct were normalized to B2M. The data are presented as the mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05 vs. indicated groups. (One-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni correction).