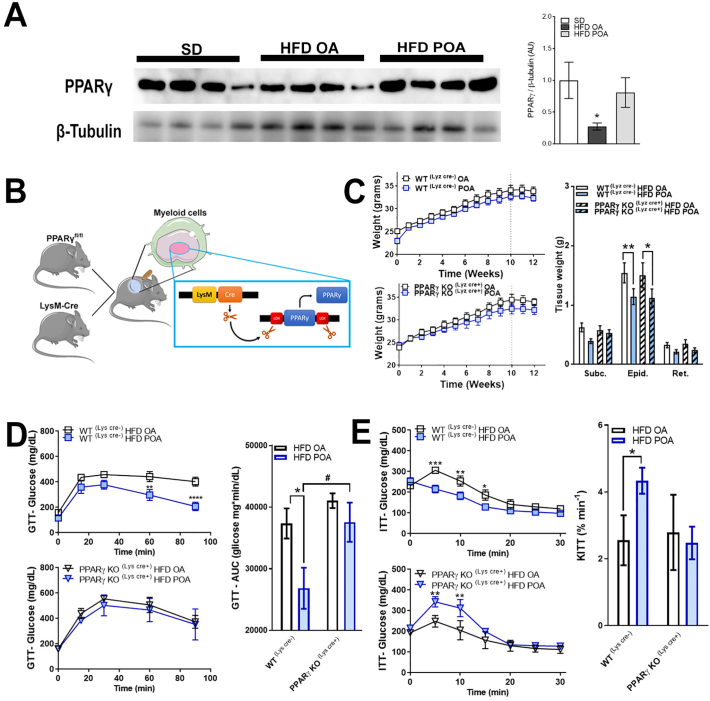
Fig. 4.
Palmitoleic acid increases PPAR-γ in liver and restores HFD-related diabetes only in WT mice, not in macrophage-specific PPAR-γ KO mice. (A) liver protein levels of peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma (PPAR-γ) normalized by the respective β-tubulin (n = 4); (B) scheme for generation of specific myeloid cell PPAR-γ knockout mice showing that PPAR-γ Flox mice were crossed with Lysozyme M-Cre (LysCre) mice; (C) body weight change during high fat diet (HFD) feeding (n = 7–10) and adipose tissue weight (n = 7–10); (D) glucose levels on glucose tolerance test (GTT) and respective area under curve (AUC) (n = 4–5); (E) glucose levels during insulin tolerance test (ITT) and respective glucose clearance constant (KITT) (n = 3–5). Wild-type (WT) mice fed with a standard diet (SD) or high-fat diet treated with oleic acid (HFD OA) or palmitoleic acid (HFD POA) (A), WT(Cre-) or PPAR-γ KO (Cre+) mice fed with high-fat diet and treated with oleic acid (HFD OA) or palmitoleic acid (HFD POA) (C, D and E). Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05 vs. indicated groups. (One-way ANOVA (A) or two-way ANOVA (C, D and E) followed by Bonferroni correction).