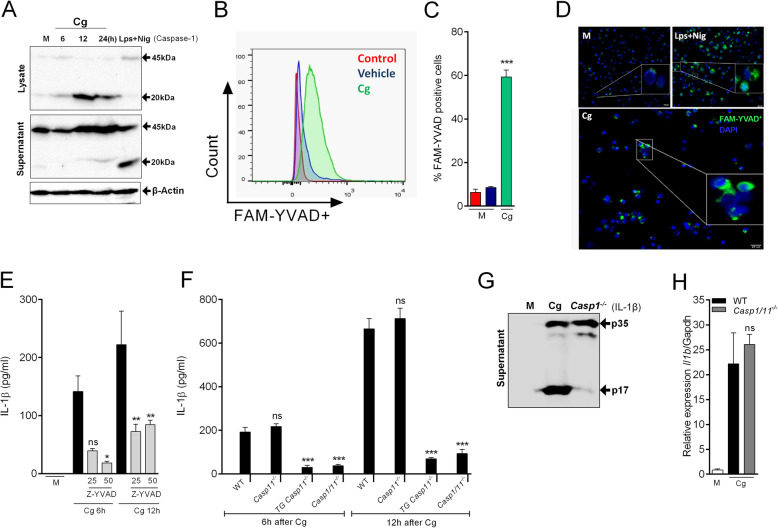
Fig. 3.
Casp1, but not Casp11, mediates IL-1β production by Cg-stimulated macrophages. Peritoneal macrophages were stimulated with Cg (300 μg/ml) or medium. a Representative western blotting for immature (p45) and active form (p20) of Caspase-1 at indicated times after Cg incubation. Beta-actin was used as a loading control. b, c Representative histogram and quantification of FAM-YVAD+ cells after Cg incubation (12 h). d Representative images of caspase-1 activity (FAM-YVAD+; green staining) after 12 h of Cg stimulation. Cell nucleus were stained with DAPI (blue). LPS primed macrophages plus nigericin was used as a positive control. e Cells were pre-incubated with a selective inhibitor of Caspase-1 (Z-YVAD) (25, 50 μM - 30 min) and then stimulated with Cg. After indicated times, the supernatants were collected for IL-1β quantification by Elisa. f Peritoneal macrophages harvested from naive WT, Casp11−/−, Casp1/11−/−, or Casp1−/−Casp11Tg mice were stimulated with Cg or medium. At indicated time points, the supernatants were collected for quantification of IL-1β by Elisa. g Representative western blotting expression of immature form (p35) and the active form (p17) of IL-1β WT vs Casp1/11−/− after Cg (24 h). h Peritoneal macrophages harvested from naive WT or Casp1/11−/− mice were stimulated with Cg or medium. After 3 h, the Il1b mRNA expression was determined by qPCR. Data are represent the mean ± SD of four independent experiments compared Control vs WT (Cg) or WT vs Knockout/Treatments groups to determine the level of statistical significance (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; and ***p < 0.001; ns, not significant)