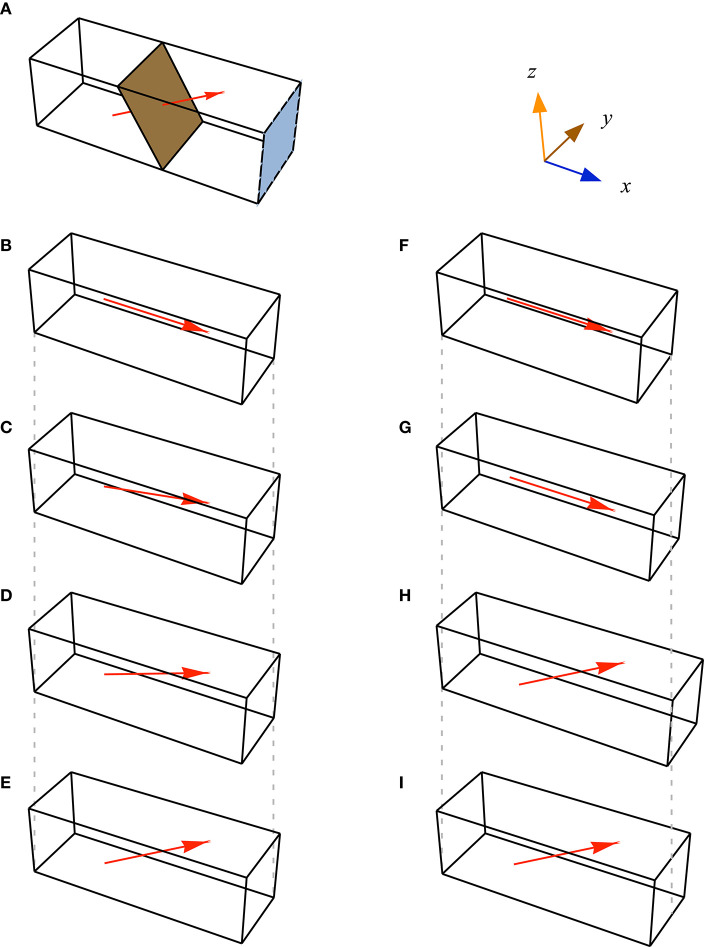
Figure 3.
Geometries of muscle blocks. (A). Each block of muscle was defined by its initial cross-sectional area (CSA, blue face, parallel to the yz plane): the physiological cross-sectional area (brown plane, normal to the fibre direction) was greater than the CSA for pennate blocks. We set fibre orientations at each quadrature point (red vector, shown here only through centre of muscle). Modelled muscle had orientations defined at 128,000 quadrature points within each block. (B–E) Some blocks had the same dimensions, but different fibre orientations. (F–I) Other blocks also varied in their CSA and volume. Vertical grey dash lines are projected down from the diagonal corners of blocks (A,F) to highlight where the other blocks have changed dimensions.