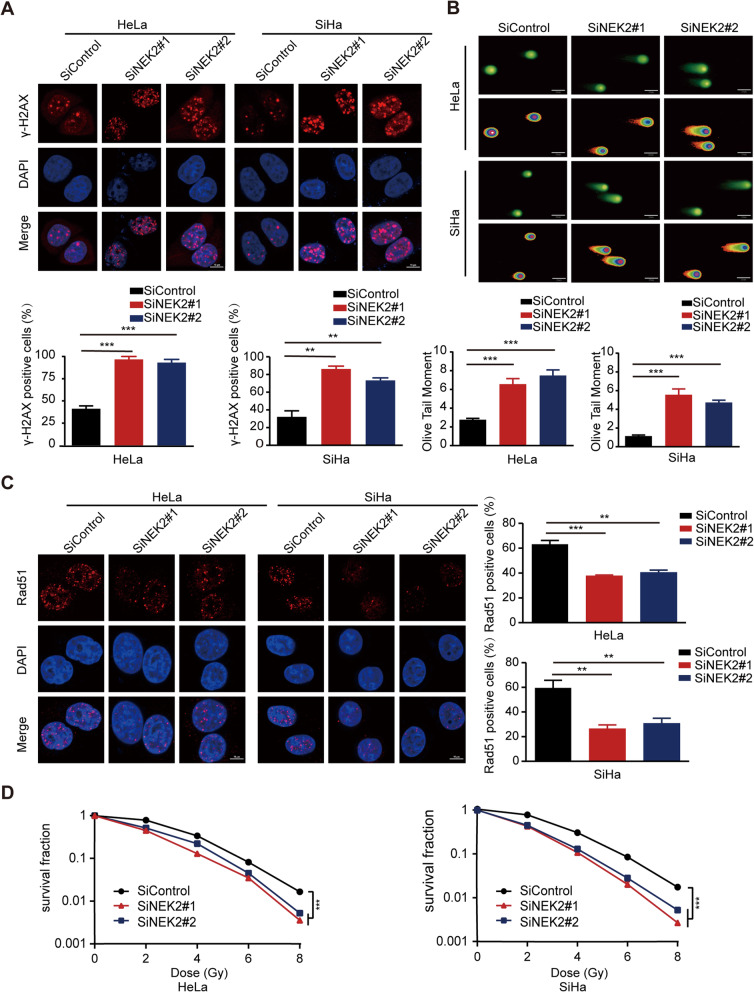
Fig. 4.
Loss of NEK2 enhances the radiosensitivity of cervical cancer cells. a Upper panel: HeLa and SiHa cells transfected with indicated siRNAs were exposed to radiation and harvested 4 h later. Immunostaining was performed to detect γ-H2AX foci formation. Lower panel: Quantification result of γ-H2AX foci was shown. Cell containing more than ten γ-H2AX foci was considered γ-H2AX-positive cell. ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001 (n = 3). Scale bar: 10 μm. b Upper panel: Representative pictures of neutral comet assay performed 4 h after IR exposure of NEK2-depleted or control cells. Lower panel: The olive tail moment was quantified and graphed. *** P < 0.001 (n = 3). Scale bar: 25 μm. c Left panel: HeLa and SiHa cells transfected with indicated siRNAs were exposed to radiation and harvested 4 h later. Immunostaining was performed to determine Rad51 foci formation. Right panel: Quantification result of Rad51 foci was shown. ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001 (n = 3). Scale bar: 10 μm. d Radiation sensitivity of HeLa and SiHa cells lacking NEK2. HeLa and SiHa cells transfected with indicated siRNAs were irradiated at indicated doses. The colonies were counted two weeks later. Data were shown as the mean ± SD. *** P < 0.001 (n = 3)