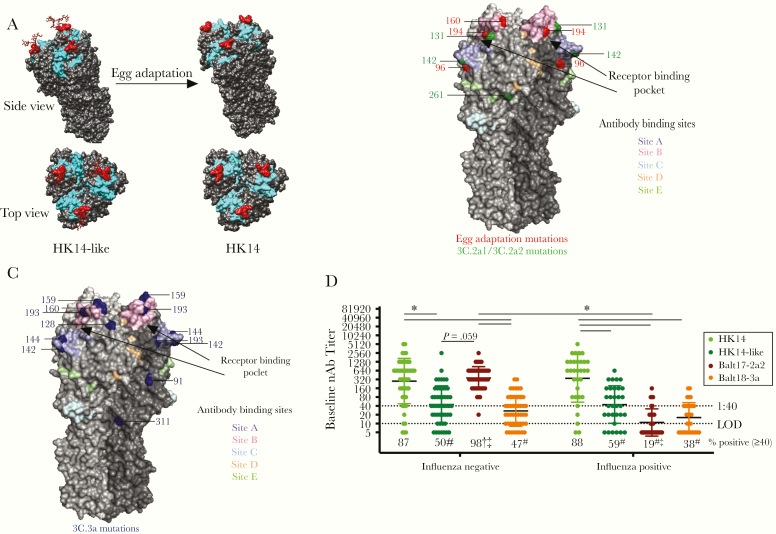
Figure 1.
The hemagglutinin (HA) of circulating H3N2 viruses lacks a key glycosylation site and includes numerous mutations as compared with the egg-adapted H3N2 vaccine strain, which differentially impacts neutralizing antibody responses to the egg-adapted vaccine virus and 2017–2018 circulating H3N2 viruses in influenza A virus (IAV)-negative and -positive patients. A, A trimer of the HA protein structure for the HK14-like and HK14 vaccine viruses are shown on a modeled H3 crystal structure (PDB: 4WE8) using University of California, San Francisco’s Chimera software. The receptor binding site is shown in cyan and the N158, T160 glycosylation site (using H3 numbering) is shown in red with a simple carbohydrate attached using GlyProt. Following passage through hen eggs, the H3 trimer of the HK14 virus lacks the glycosylation site at the T160K position, marked in red. B, A trimeric HA protein structure of H3N2 viruses is shown using an H3 crystal structure of A/Aichi/2/1968 (PDB: 2YPG) using PyMOL. The 5 major antigenic sites A, B, C, D, and E are indicated in pastel purple, pink, blue, orange, and green, respectively [20–22]. The sialic acid (SA) receptor binding pocket is between sites A and B, which are indicated with black arrows [23]. Mutations that arose in egg adaptation are marked in red, while amino acid differences in the 3C.2a2 viruses compared to the HK14-like (3C.2a) virus are shown in green. C, Amino acid differences in 3C.3a compared to 3C.2a are marked in blue using PyMOL (PDB: 2YPG). D, Serum collected at enrollment (baseline) from H3N2-infected individuals was used to perform microneutralization assays to measure neutralizing antibody (nAb) titers in both IAV-negative (n = 49) and IAV-positive (n = 32) patients against the egg-adapted HK14 vaccine and cell-grown HK14-like viruses and the Balt17-2a2 and Balt18-3a circulating H3N2 viruses. Significant differences in nAb titers against the HK14 relative to the HK14-like or circulating H3N2 viruses as well as between IAV-negative and IAV-positive patients for an individual virus are represented with *. The limit of detection (LOD) is labeled with a stippled line at 1:10 dilution and the World Health Organization cutoff for seroprotection is indicated with a stippled line at 1:40. The percentage of patients with nAb titers > 1:40 is indicated below each virus. For both the IAV-negative and IAV-positive patients, significant differences in the proportion of patients with a ≥ 1:40 nAb titer against the HK14 virus relative to the HK14-like or circulating viruses are indicated with #. For an individual virus, significant differences in the proportion of IAV-positive and IAV-negative patients are illustrated with †, and significant differences in proportions between circulating viruses to the HK14-like cell-grown viruses are shown with ‡.