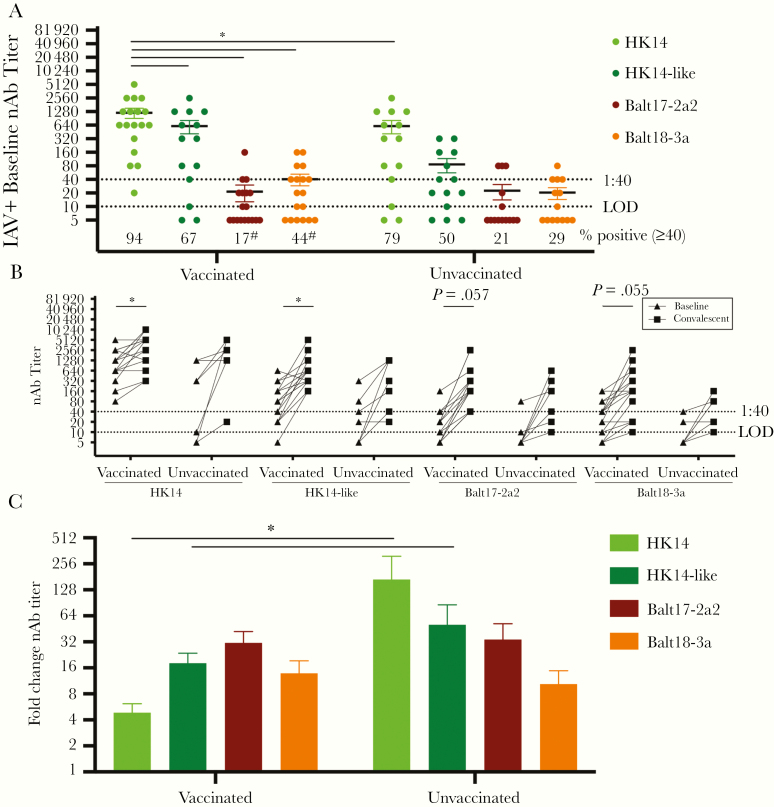
Figure 5.
Among influenza A virus (IAV)-positive patients, vaccination increased baseline neutralizing antibody (nAb) titers to the H3N2 vaccine relative to circulating H3N2 viruses resulting in reduced seroconversion during convalescence in the 2017–2018 season. A, Baseline serum samples from vaccinated and unvaccinated patients were used to measure neutralizing antibody (nAb) titers against the HK14 and HK14-like H3N2 vaccine viruses and the Balt17-2a2 and Balt18-3a circulating viruses during the 2017–2018 influenza season. The limit of detection (LOD) is labeled with a stippled line as is the cutoff for seroprotection (1:40). The percentage of patients with nAb titers > 1:40 is indicated below each virus. For both vaccinated and unvaccinated IAV-positive patients, significant differences in the proportion of patients with a > 1:40 nAb titer against the HK14 virus relative to the HK14-like or circulating viruses are indicated with #. B, Baseline and convalescent nAb titers from each IAV-positive vaccinated and unvaccinated patient. C, The fold change in nAb titers (convalescent divided by baseline) for vaccinated and unvaccinated patients for each virus. Significant differences in nAb titers against the HK14 relative to the HK14-like or circulating H3N2 viruses (A), between baseline and convalescent samples (B), and between vaccinated and unvaccinated IAV-positive patients (C) are represented with *.