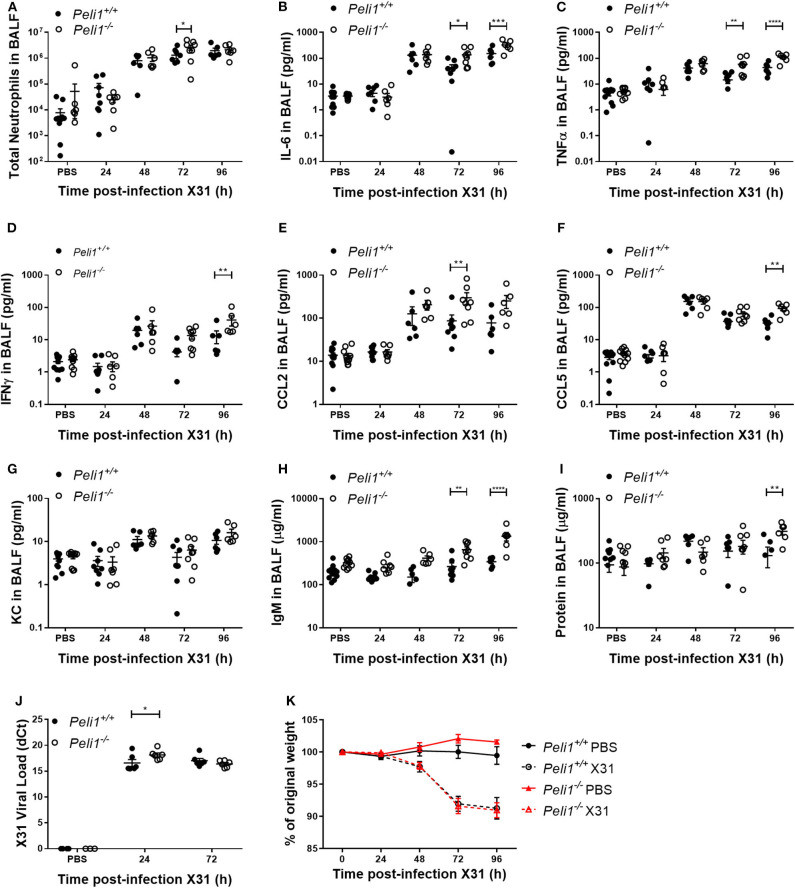
Figure 4.
Peli1−/− mice exhibit enhanced proinflammatory responses and airway damage to influenza A infection, without loss of viral replication. Peli1−/− mice and age- and sex-matched wild type littermate controls were given a single dose of 5 × 103 PFU influenza A X31 or PBS (control) i.n. under gaseous anesthesia. Animals were sacrificed and lavaged at the time points indicated, and total cell number in BALF enumerated by haemocytometer, with the number of neutrophils determined by differential cell counts calculated by microscopic analysis of cytospin preparations (A). Levels of the cytokines IL-6 (B), TNFα (C), IFNγ (D), CCL2 (E), CCL5 (F), and KC (G) in BALF were determined by CBA. IgM levels (H) in BALF were determined by ELISA. Total protein levels (I) in BALF were determined by Bradford assay. X31 viral load (J) was determined by qRT-PCR of homogenized whole lung. Animals were weighed daily, and weight loss is shown as a percentage of original weight (K). Individual data points (A–J) show a single mouse, and data panels (A–K) show mean ± SEM; Peli1+/+ mice PBS n = 12, X31 24 h n = 8, X31 48 h n = 6, X31 72 h n = 8, X31 96 h n = 6; Peli1−/− mice PBS n = 11, X31 24 h n = 7, X31 48 h n = 6, X31 72 h n = 8, X31 96 h n = 6. Significant differences between groups are indicated by *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001, as measured by two-way ANOVA with Sidak's post-test (statistical analysis was conducted upon dCt values for qRT-PCR data).