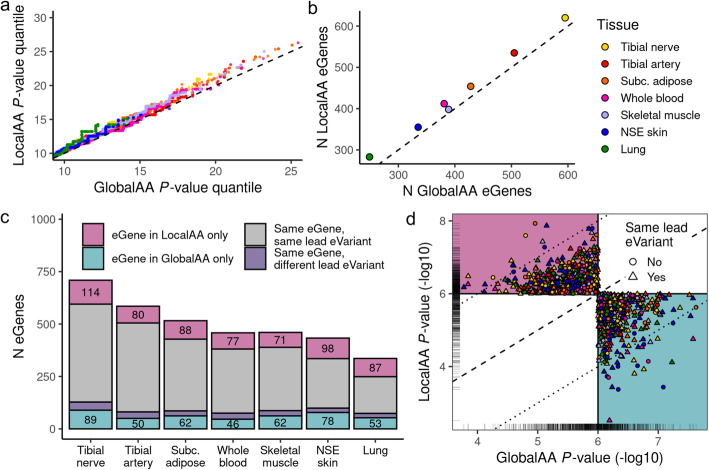
Fig. 2.
Comparison of cis-eQTLs called by LocalAA or GlobalAA. Cis-eQTL mapping was performed in seven tissues. A nominal P value threshold of 1e−6 was applied to identify significant associations. a A Q-Q plot of nominal P values for all tests indicates a modest improvement of power in most tissues when using LocalAA. b LocalAA identifies more eGenes than GlobalAA in all seven tissues (P value = 0.0078, binomial probability). c The majority of eGenes are identified by both ancestry adjustment methods (gray + purple). The two methods report different eVariants for a small fraction of these eGenes (purple). Numbers indicate eGenes uniquely called by one of the ancestry adjustment methods, which are plotted in d. d The majority of eGenes unique to one ancestry adjustment method fall near the significance threshold, as indicated by the rug plot. Dotted lines demarcate the region outside of which eGenes in one method have a nominal P value at least two orders of magnitude more significant than the alternate method. Points are colored by tissue