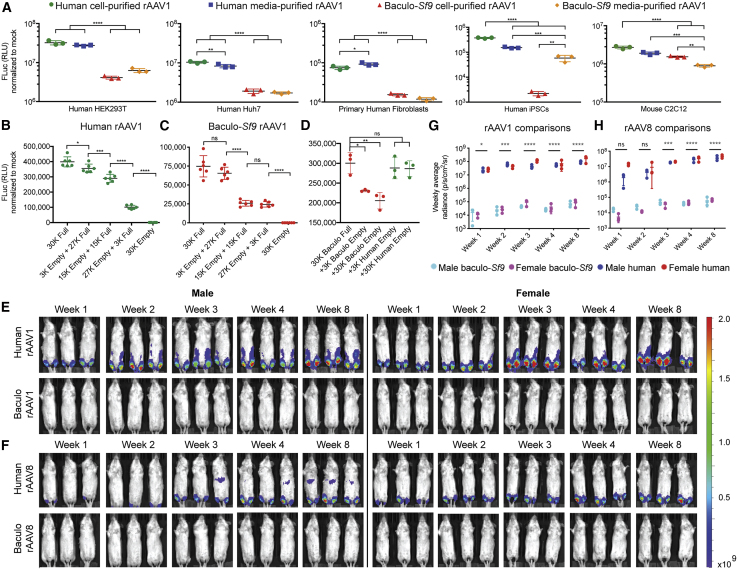
Figure 4.
rAAV Produced with the Human Platform Is More Potent In Vitro and in Skeletal Muscle In Vivo following Intramuscular Administration
(A) In vitro functional transduction assays in immortalized human HEK293T and Huh7 cells, primary human fibroblasts, primary human iPSCs, and immortalized mouse C2C12 myoblasts transduced with ssAAV1-EF1α-FLuc. Human-produced rAAV1 was significantly more potent than similar baculovirus (baculo-)Sf9 vector in all cases. (B) HEK293T cells were transduced with varying ratios of full/empty human-produced ssAAV1-EF1α-FLuc with the total capsid content kept constant at an MOI of 30,000, while the ratio of full/empty varied. FLuc assays were performed on cell lysates 3 days post-transduction and normalized to mock-transduced wells. Each green dot represents one replicate; mean ± SD is shown. (C) Same as (A) except using baculo-Sf9 rAAV1. (D) To further assess the impact of insect HCP impurities, HEK293T cells were transduced with a fixed MOI of 30,000 of full baculo-produced ssAAV1-EF1α-FLuc and spiked with an additional 10% or 100% of empty baculo-produced or empty human-produced vector. FLuc assays were performed on cell lysates 3 days post-transduction and normalized to mock-transduced wells. Each dot represents one replicate; mean ± SD is shown. (E) In vivo time course functional transduction assays comparing human and baculovirus-Sf9 ssAAV1-EF1α-FLuc after i.m. administration (5e10 vg/mouse) in age-matched siblings. Mean radiance (photons/s/cm2/sr) displayed with all mice imaged on their ventral side on the same shared scale. (F) Same as (E) but with ssAAV8-EF1α-FLuc; same shared scale as (E). (G) Quantification of rAAV1 FLuc radiance from (E). Each symbol represents mean signal (±SD) from three mice. (H) Same as (G) but with rAAV8. ∗p ≤ 0.05, ∗∗p ≤ 0.01, ∗∗∗p ≤ 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p ≤ 0.0001.