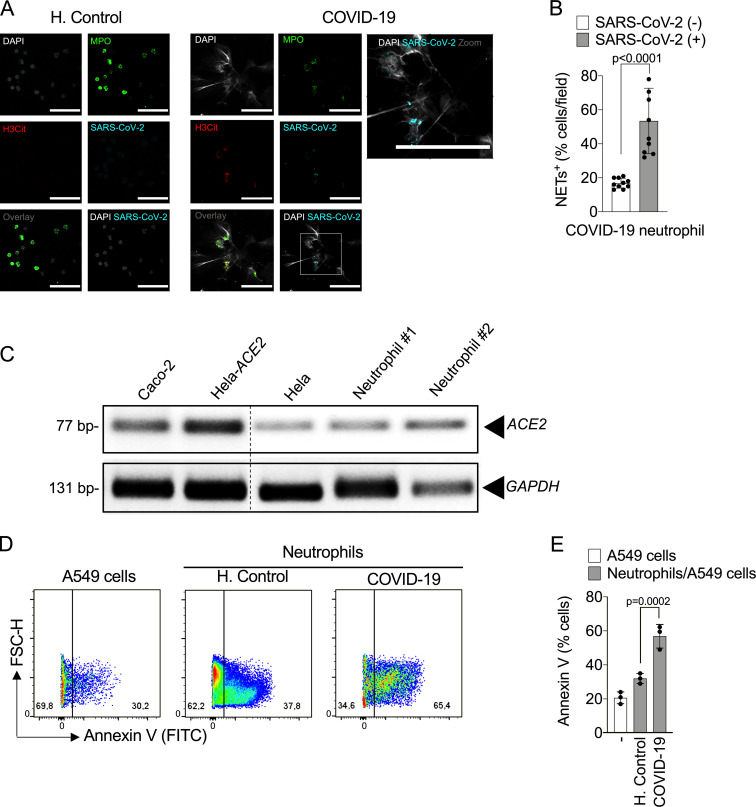
Figure S2.
Infected neutrophils from COVID-19 patients induce apoptosis in lung epithelial cells. (A) Representative confocal images showing the detection of SARS-CoV-2 antigens in blood neutrophils from COVID-19 patients (n = 5), but not in neutrophils from healthy controls (H.Control; n = 5). Cells were stained for nuclei (DAPI, white), MPO (green), H3Cit (red), and SARS-CoV-2 (Cyan). Scale bar indicates 50 µm. (B) Percentage of NET-positive cells stained, or not, for SARS-CoV-2 antigens. Blood-isolated neutrophils (106 cells) from healthy controls (n = 3) or COVID-19 patients (n = 3) were co-cultured with A549 lung epithelial cells (5 × 104 cells) for 24 h at 37°C. (C) Expression of ACE2 was assessed by conventional PCR (C) in Caco-2, HeLa cells transduced with hACE2 (Hela-ACE2), HeLa cells, and isolated neutrophils from healthy controls. GAPDH expression was used as load control for gene expression. The samples were run on the same gel and the dotted line represents unrelated lanes. (D) Representative dot plots of FACS analysis for A549 Annexin V+ cells. (E) Frequency of Annexin V+ A549 cells. Data are representative of at least two independent experiments and are shown as mean ± SEM. P values were determined by two-tailed unpaired Student t test (two fields/patient; B) or one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post hoc test (E).