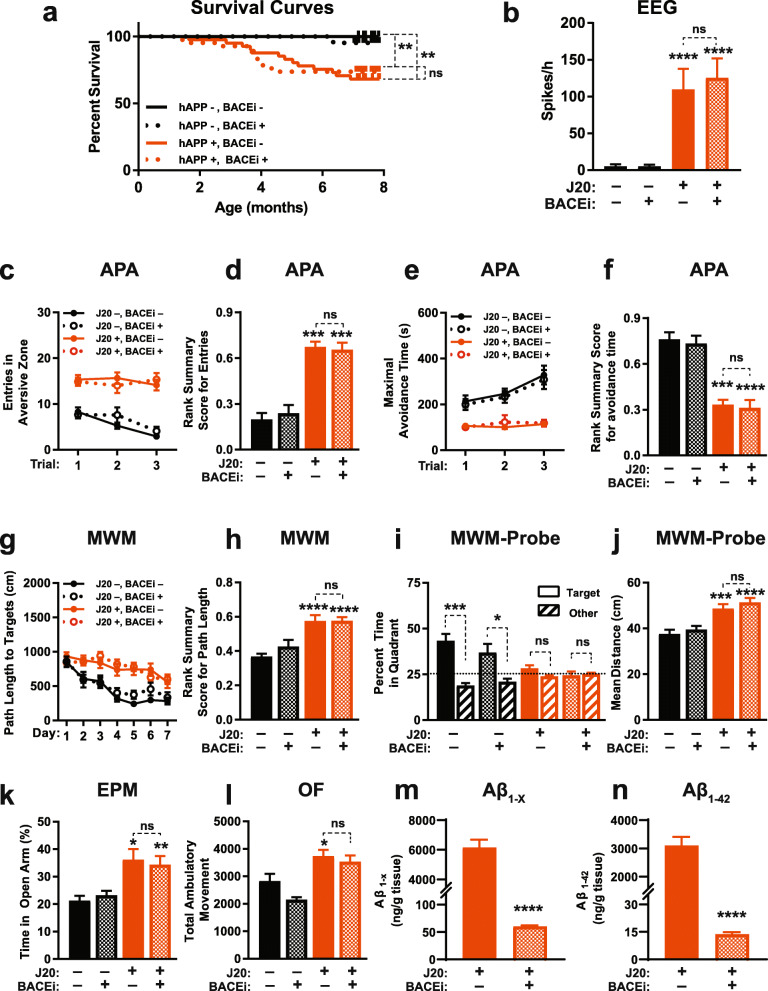
Fig. 8.
Early BACEi treatment does not prevent functional abnormalities in J20 mice. a–l J20 mice (+) and WT (−) controls were treated with the BACEi NB-360 (+) or placebo (−) starting at 1 month of age and continuing throughout the observation period (a), behavioral testing at 4–6 months (c–l), EEG recordings at 6–7 months (b), and hippocampal Aβ measurements at 7–8 months (m, n) of age. a Survival curves. **P < 0.01 or not significant (ns) as indicated by brackets, based on Mantel-Cox log-rank test. The trend toward an acceleration in mortality in BACEi-treated J20 mice around 4 months was not statistically significant (P = 0.07, based on log-rank test applied to data of mice from either J20 group that survived at least 4 months). b Epileptiform spike frequencies determined in resting mice during 8-h recording periods. c–f Learning and memory in the active place avoidance (APA) test was quantified as in Fig. 6a–d. g, h Learning behavior in the Morris water maze (MWM) test was reflected by reductions in the path length that mice required to locate a hidden platform (g) and was quantitated by a rank summary score (h), which was calculated as described in Methods. i, j Spatial learning and memory retention were assessed in a probe trial 24 h after the last training trial, in which we determined whether mice favored the quadrant in which the platform was previously located (i) and their mean distance from the original target location averaged over each second of the probe trial (j). The target preference index was calculated by dividing the percentage of time mice spent in the target quadrant by the percentage of time they spent in non-target quadrants. k Percentage of time mice spent in the open arms of an elevated plus maze (EPM). l Locomotor activity in the open field (OF) was recorded for 15 min. (m, n) Hippocampal levels of Aβ1-x (m) and Aβ1–42 (n) were determined by ELISA. Three behaviorally tested J20 mice (2 BACEi-treated and 1 placebo-treated) were not included in this analysis because they died after the behavioral testing and before Aβ measurements could be carried out. n = 21–42 (a), 11–16 (b), 11–17 (c–f), 12–17 (g–l), and 14–15 (m, n) mice per group. All groups in (a) included males and females, whereas groups in (b–n) consisted of males only to reduce variability in behavioral performance. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001 vs. placebo-treated WT or as indicated by brackets, based on two-way ANOVA with Holm-Sidak correction (b, h, i, j), Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn correction (d, f, l), multiple Welch t-tests with Holm-Sidak correction (k), or two-tailed unpaired t test with (m) or without (n) Welch’s correction. Values are means ± SEM