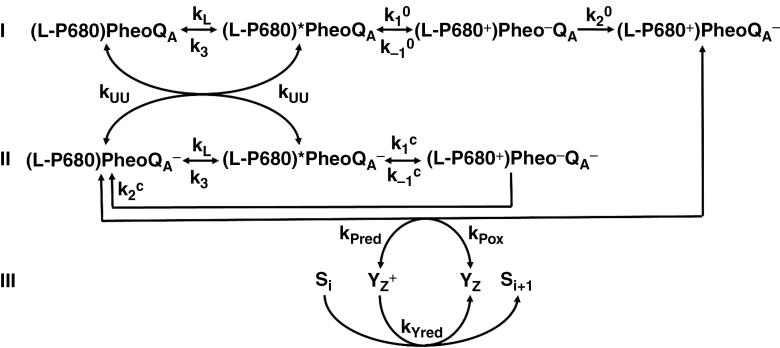
Fig. 2.
Scheme showing the RRP (reversible radical pair) model and related reactions. The original RRP model is represented by the reactions on lines I and II, which are reactions occurring in an open PSII RC (when QA is initially oxidized) and a closed PSII RC (when QA is initially reduced), respectively. (L–P680)* denotes Chls in the light harvesting antenna of PSII (L) plus P680, which are in ultrafast excitation kinetic equilibrium, the asterisk (*) indicating the excited state. The rates constants are: kL, overall rate constant of antenna excitation; k3, overall rate constant of the excited state deactivation through heat dissipation and ChlF emission; k1o and k1c, rate constants of the primary charge separation in open and closed PSIIs, respectively; k-1o and k-1c, rate constants of the radiative (i.e. to the excited state) charge recombination between P680+ and Pheo− in open and closed PSIIs, respectively; k2o, rate constant of charge stabilization in an open PSII, i.e. the ET from Pheo‒ to QA; k2c, rate constant of non-radiative (i.e. to the ground state) charge recombination between P680+ and Pheo‒ in a closed PSII. The scheme presented here also includes excitation energy transfer (the energetic connectivity) between open and closed PSIIs (rate constant kUU) and reversible reduction of P680+ by YZ (rate constants kPred and kPox), as well as the reduction of YZ+ by the manganese cluster of the oxygen-evolving complex (OEC; rate constant kYred), which produces an S-state transition from Si to Si+1, where Si and Si+1 represent particular S-states. Modified from Lazár and Schansker (2009).