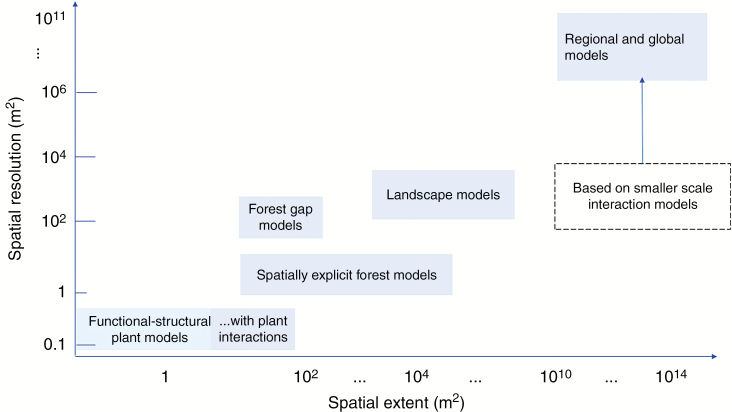
Fig. 1.
Types of ABMs with the ranges of spatial extent and resolution. (1) Functional structural plant models (FSPMs): for example, PEACH (Grossman and DeJong, 1994), and Tomato model (Sarlikioti et al., 2011). (2) FSPMs with plant–plant interactions: for example, PLATHO (Gayler et al., 2006), Virtual Grassland (Louarn et al., 2020, ROOTMAP (Diggle, 1988). (3) Gap phase models: for example, JABOWA (Botkin et al., 1972), FORET (Shugart and West, 1977), LINKAGES (Post and Pastor, 1996), FORMAN (Chen and Twilley, 1998), EDS (Ngugi et al., 2011) and FORCLIM (Bugmann and Solomon, 2000). (4) Spatially explicit forest models: for example, SORTIE (Pacala et al., 1993), MANGRO (Berger et al., 2008) and TROLL (Maréchaux and Chave, 2017). (5) Landscape models (linking gap models): for example, ZELIG (Miller and Urban, 1999), LANDIS (Mladenoff, 2004), FORMIND (Kohler and Huth, 1998), TREEGRASS (Simioni et al., 2000) and PSS (Fennel et al., 2012). (6) Regional models: for example, SEIB-DDVM (Sato et al., 2007) and ED (Moorcroft et al., 2001).