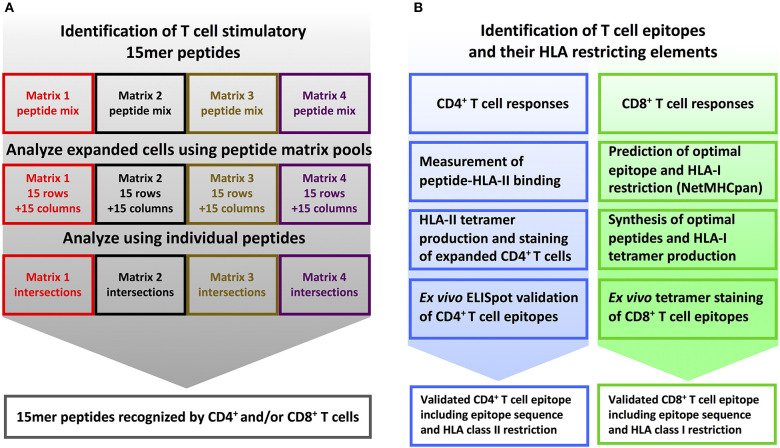
Figure 2.
T cell epitope screening strategy. (A) Identification of stimulatory 15mer peptides: PBMC's from YFV vaccinated donors were divided into four cultures and in vitro stimulated with peptide sublibraries corresponding to each of the four 15 × 15 peptide matrices. After 8 days, each sublibrary expanded PBMC culture was tested by ICS against the matrix-specific row and column peptide pools. Subsequently, individual peptides representing stimulatory matrix intersections were analyzed to identify single T cell stimulatory 15-mer peptides. (B) Identification of T cell epitopes and their HLA restriction elements: CD4+ T cell epitope deconvolution: Single CD4+ T cell stimulatory 15mer peptides were tested for binding to the donor's HLA-DR molecules using a biochemical HLA class II binding assay, positive interactions were used to generate peptide-HLA class II tetramers, and these tetramers were used to stain expanded T cells, and the resulting epitopes were eventually validated by ex vivo ELISpot analysis. CD8+ T cell epitope deconvolution: Single CD8+ T cell stimulatory 15mer peptides were submitted to the NetMHCpan 2.4 predictor together with the donor's HLA class I haplotype to identify optimal epitopes and their HLA-restriction elements. These optimal epitopes were subsequently synthesized and validated by ex vivo peptide-HLA class I tetramer staining.