Figure 1. General Causal Mediation Analysis and Magnitude of Changes in Behavior After Treatment of Obstructive Sleep Apnea.
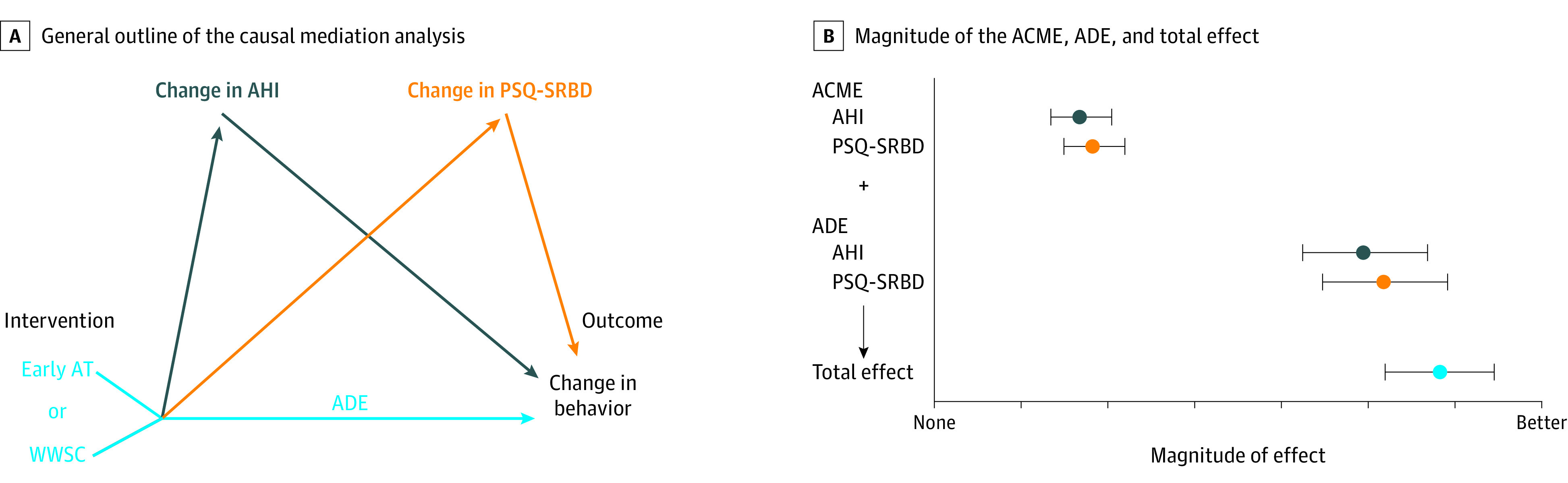
A, The average causal mediation effect (ACME) were the changes in a mediator variable (eg, Apnea Hypopnea Index [AHI] or the Pediatric Sleep Questionnaire–Sleep-Related Breathing Disorder [PSQ-SRBD] score) after the intervention (early adenotonsillectomy ([AT] vs watchful waiting with supportive care) was provided. The magnitude of ACME was obtained from the products of the coefficients of the 2 regressions (mediator modeled by the intervention and outcome modeled by the mediator) after controlling for potential confounders. The average direct effect (ADE) was the outcome of treatment that was not attributable to the putative mediation pathways. The ACME and ADE provided the total effect, which was estimated as the size of the intervention effect. B, The magnitude of the ACME, the ADE, and the total effect is shown with the error bars representing the associated bootstrapped measure of uncertainty (95% CIs).
