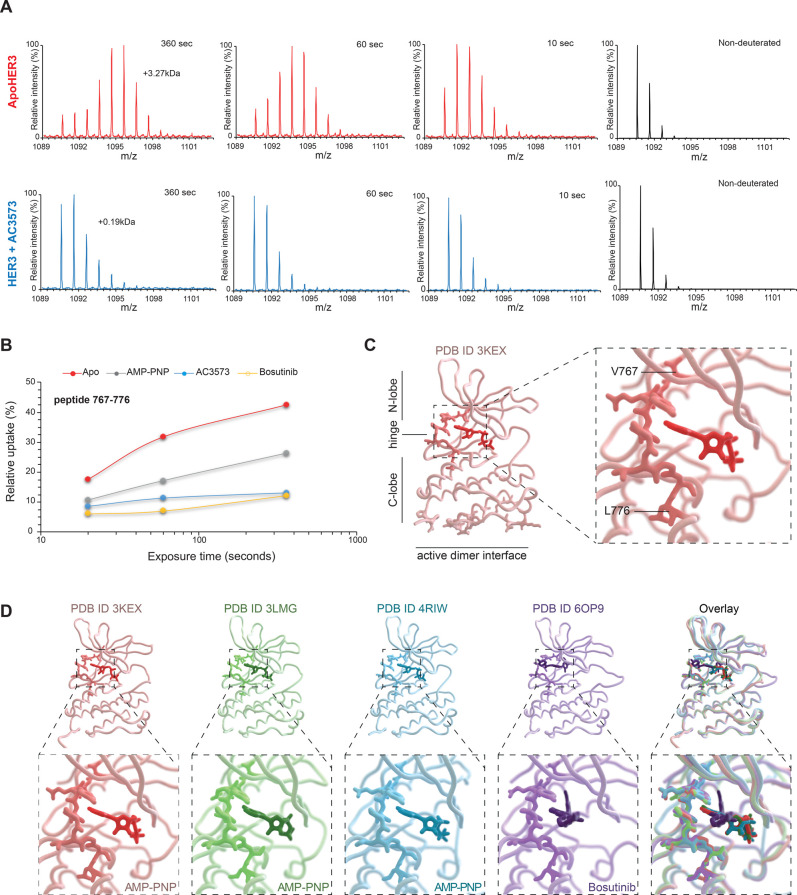
Figure 4. HDX-MS identified HER3 nucleotide-binding pocket region as AC3573 binding site.
(A) Differences in deuterium incorporation between ApoHER3 (HER3 no ligand) and HER3 in the presence of AC3573. Mass spectra of the peptide 767–776 for ApoHER3 (left, in red) and HER3 + AC3573 at 100 μM (right, in blue) are shown, as non-deuterated and for deuterium labelling times of 10 s, 1 min and 6 min. Levels of deuteration are determined through comparison of the average mass from the intensity-weighted centroid m/z value of the peptide. The mass spectra show that the peptide 767–776 has an increase in mass of 3.27 kDa following deuterium incorporation for ApoHER3, compared with an increase in 0.19 kDa for HER3 incubated with AC3573. (B) The deuterium uptake (as relative uptake in %), resolved for peptide 767–776, plotted at various time points for ApoHER3 and HER3 incubated with 100 μM of AMP-PNP, bosutinib or AC3573. Deuterated sample data were obtained in triplicate for all three deuterium uptake time points. The protection of the peptide comprising residues 767–776 suggests AMP-PNP, bosutinib and AC3573 have the same binding site to HER3. (C) Left: crystal structure of HER3 bound to AMP-PNP (PDB:3KEX), showing AC3573 compound binding site (highlighted). Right: close up of AC3573 binding site (highlighted), corresponding to peptide 767–776 VTQYLPGSL, encompassing the hinge region. (D) Individual structures of HER3 tyrosine kinase domain (amino acids 684–1020) bound to AMP-PNP (PDB:3KEX and PDB:3LMG), to bosutinib (PDB:6OP9) and in the context of EGFR/HER3 kinase domain heterodimer (PDB:4RIW) and structural alignments (overlay) of these four crystal structures showing that AC3573 binding site (highlighted as heavier backbone chain in each structure) is the hinge peptide capping the nucleotide-binding pocket.