Figure 6.
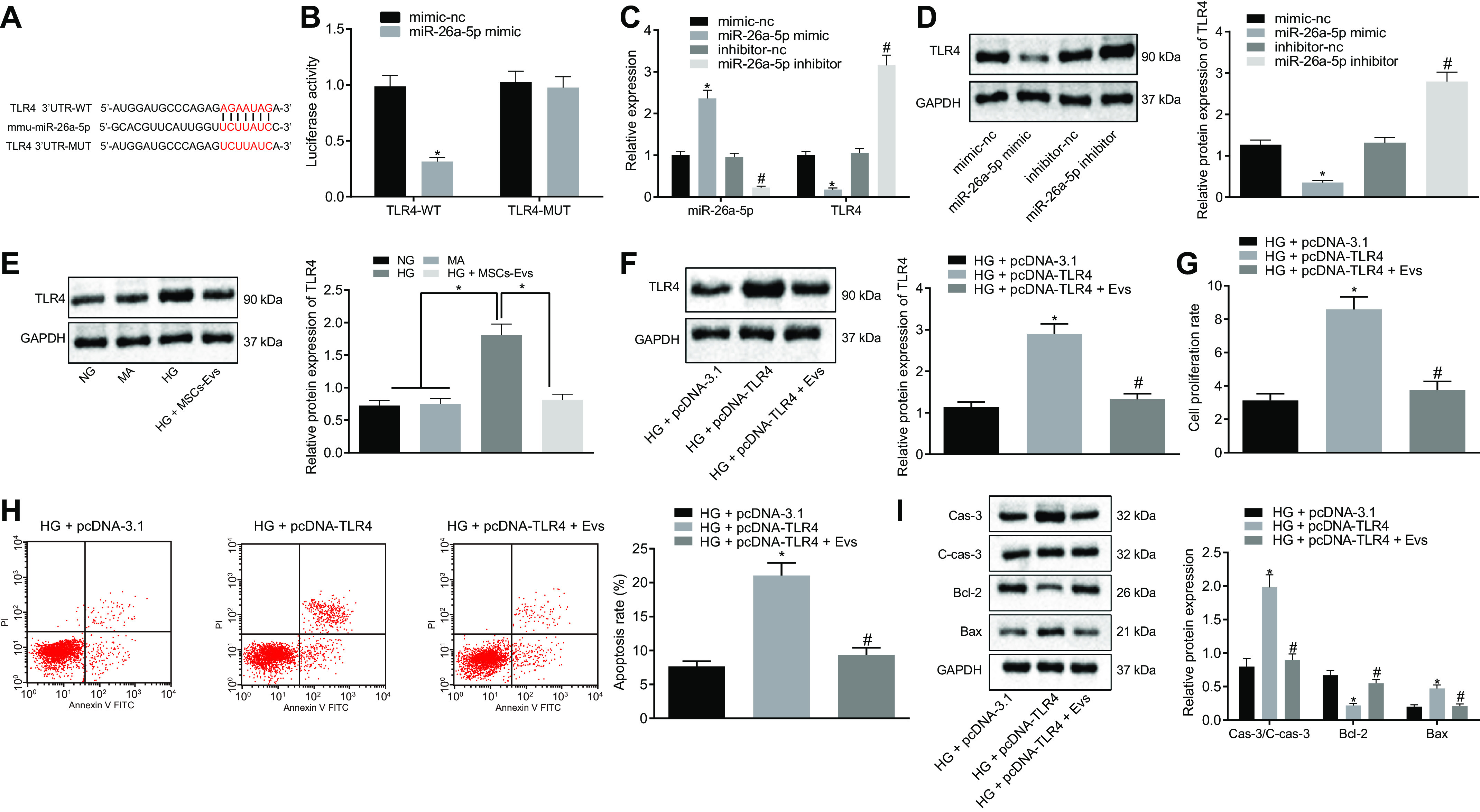
MiR-26a-5p transferred by ADSCs-derived EVs targets TLR4 to inhibit apoptosis of MP5 cells induced by HG. A, the specific binding sites of TLR4 and miR-26a-5p predicted by the TargetScan website (RRID:SCR_010845). *, p < 0.05. B, Dual-Luciferase reporter gene assay confirms TLR4 as a target of miR-26a-5p. *, p < 0.05 versus mimic-NC + TLR4 3'UTR-WT. C, the expression of miR-26a-5p and TLR4 in MP5 cells as detected by RT-qPCR. *, p < 0.05 versus mimic-NC. #, p < 0.05 versus inhibitor-NC. D–F, the protein expression of TLR4 in MP5 cells as detected by Western blot analysis, normalized to GAPDH. G, MP5 cell viability as detected by CCK-8 assay. H, the apoptosis of MP5 cells as detected by flow cytometry. I, the protein expression of apoptosis related proteins (caspase-3, cleaved caspase-3, Bcl-2, Bax) in MP5 cells as detected by Western blot analysis, normalized to GAPDH. Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation. Comparisons between two groups were analyzed using unpaired t test. Data among multiple groups were compared using one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey's post hoc test. The experiment was repeated three times. In panel D, *, p < 0.05 versus mimic-NC. #, p < 0.05 versus inhibitor-NC. In panel E, *, p < 0.05 versus NG or MA or HG + MSCs-Exo. In panels F–I, *, p < 0.05 versus HG + pcDNA-3.1. #, p < 0.05 versus HG + pcDNA-TLR4.
