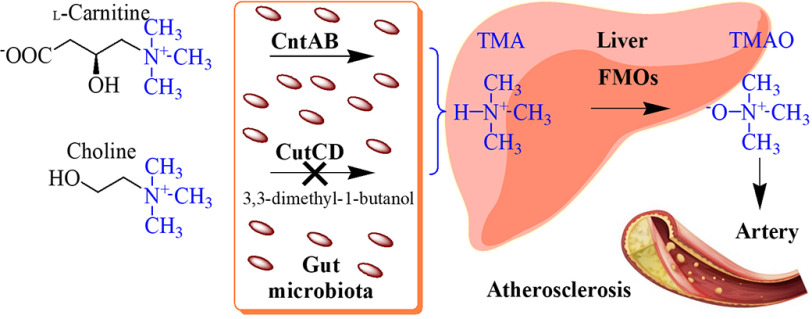
Figure 1.
Gut microbiota and metabolism of dietary nutrients associated with atherosclerosis. The gut microbiota makes use of dietary nutrients l-carnitine and choline as carbon and energy sources. The C-N bond of these compounds is cleaved by TMA lyases. The resulting TMA molecule is further metabolized in the human liver by flavin monooxygenases (FMOs) of the host. The synthesized TMAO molecule was shown to enhance atherosclerosis development. In multiple human studies, elevated TMAO levels have been associated with cardiovascular diseases and the risks for myocardial infarction and stroke. For the TMA lyase CutCD, an efficient targeted inhibitor was identified that prevented the formation of TMA in mouse models.