Figure 2.
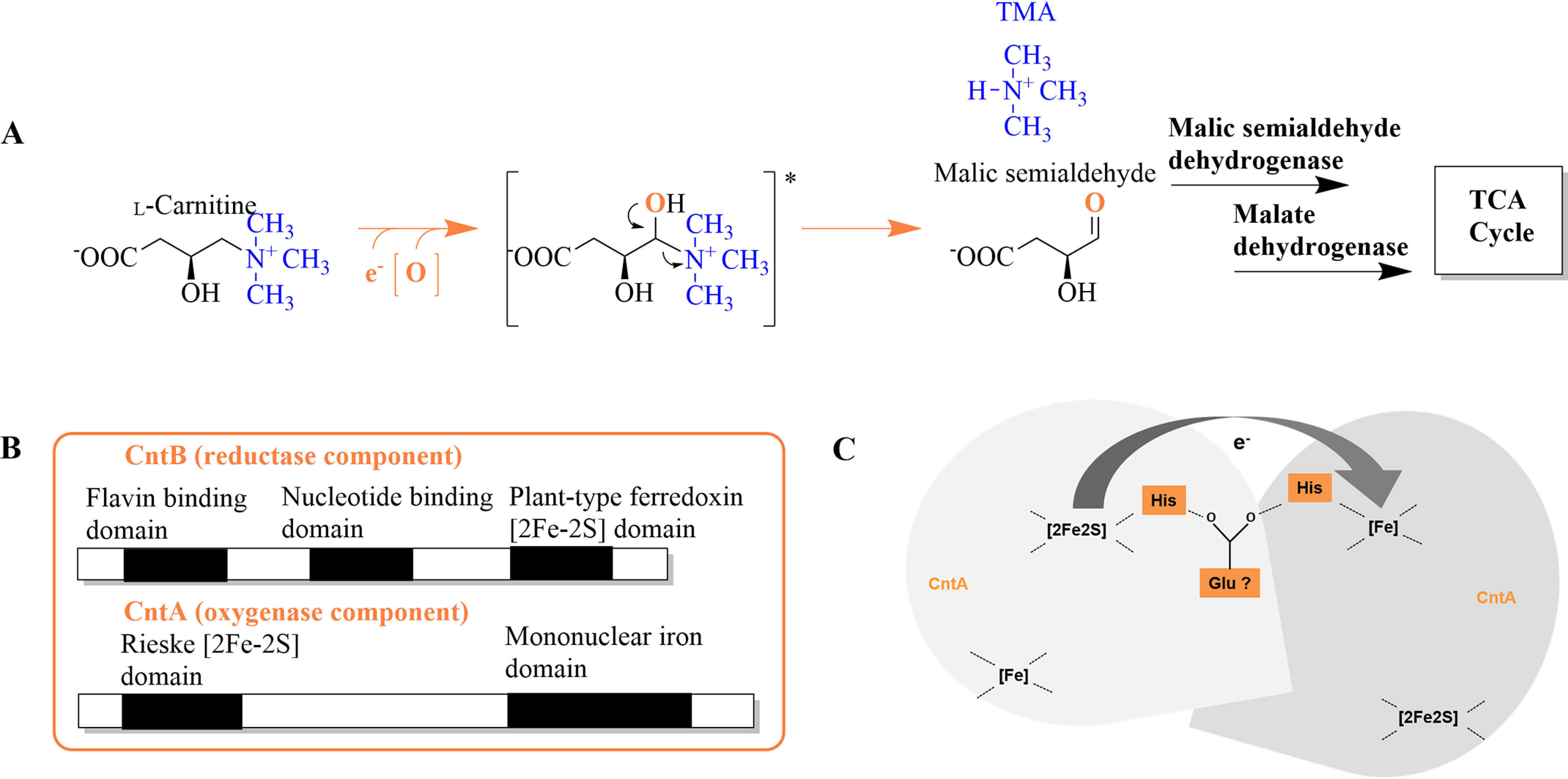
Synthesis of TMA and malic semialdehyde from l-carnitine, postulated domain architecture of CntA and CntB, and proposed electron transfer between subunits of CntA. A, conversion of l-carnitine via a proposed hydroxyl-intermediate (*) into TMA and malic semialdehyde, which is channeled into the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle via malic semialdehyde dehydrogenase and malate dehydrogenase. B, theoretical sequence analyses revealed motifs of a flavin binding domain, nucleotide binding domain, and plant-type ferredoxin [2Fe-2S] domain in sequences of CntB and of a Rieske [2Fe-2S] and a mononuclear iron domain in CntA. C, schematic depiction of the proposed intersubunit electron transfer via a bridging glutamate residue from the Rieske [2Fe-2S] onto the mononuclear iron center of CntA.
