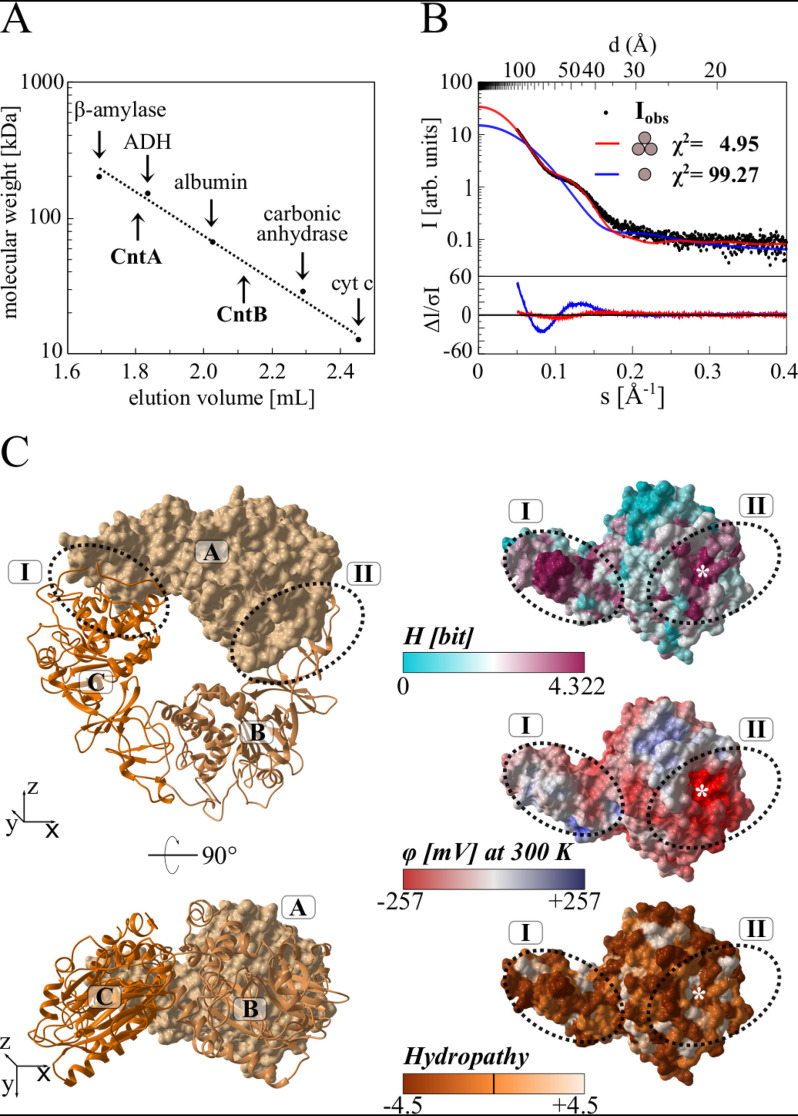
Figure 5.
Relative molecular weight of CntA and CntB, small-angle X-ray scattering, and homology modeling of the functional CntA trimer. A, native molecular weight determination of CntA and CntB by analytical gel filtration. Purified proteins were analyzed on a Superdex 200 increase 5/150 GL column at a flow rate of 0.5 ml min−1, monitoring the absorption at 280 nm. Protein standards β-amylase (Mr = 200,000), alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH, Mr = 150,000), albumin (Mr = 66,000), carbonic anhydrase (Mr = 29,000), and cytochrome c (Mr = 12,400) were used for calibration. B, small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) analysis of CntA. Experimental SAXS data from a CntA solution (black dots) were related to the simulated SAXS curves of a potential monomeric (blue) or trimeric (red) structural model. The χ2 value reflects the fit quality with respect to the experimental data (best fit for CntA trimer). C, homology modeling of the CntA trimer. The Phyre server was used to predict a structural model of monomeric CntA. This model was superimposed onto the structure of the trimeric aromatic-ring hydroxylating dioxygenase (PDB code 3N0Q). The resulting CntA trimer (ABC) is depicted in two orientations as a surface/cartoon representation (left). Related interface regions I and II (dotted ovals) revealed a high degree of surface conservation (indicated as Shannon entropy H, ranging from 0 to 4.322 bit, top right). Both regions indicate an opposed electrostatic surface potential (φ, from −257 to +257 mV, middle right) and no increased hydropathy (−4.5 to 4.5, bottom right). The theoretical position of Glu-205 at the interface is indicated by an asterisk.