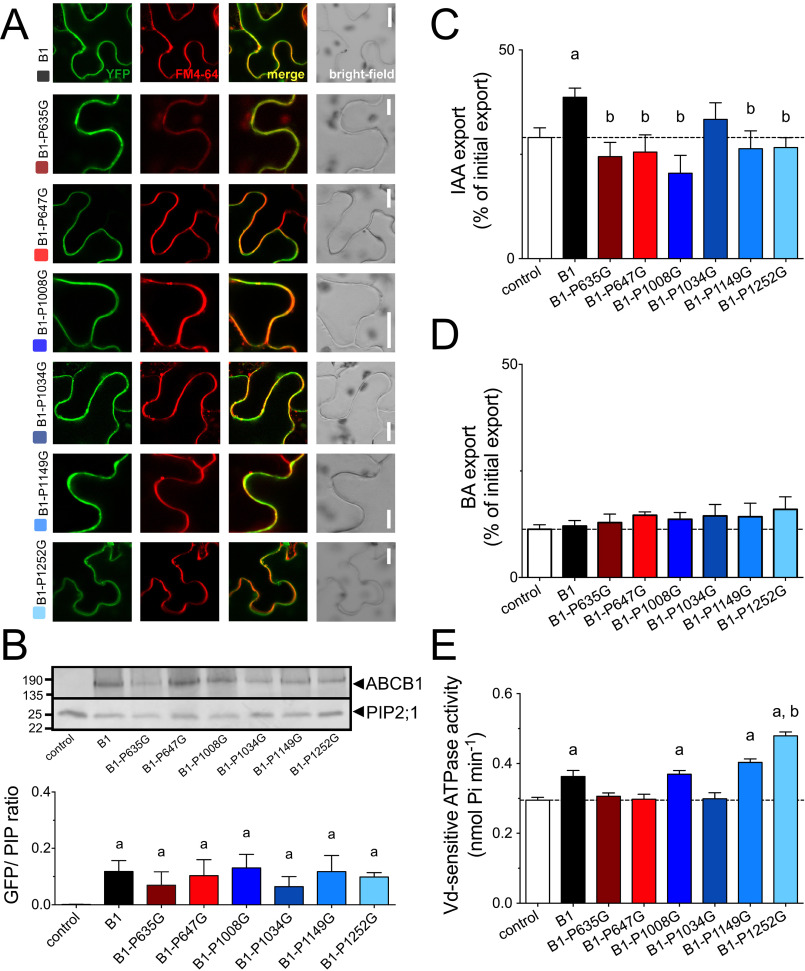
Figure 2.
Mutation of most surface-exposed prolines in ABCB1 reduces IAA export. A, mutation of six surface-exposed prolines does not significantly alter expression and PM as revealed by confocal imaging of ABCB1-GFP of tobacco leaves transfected with ABCB1-GFP and stained with PM marker, FM4-64. Bars, 10 μm. B, proline mutation of ABCB1 does not significantly alter expression levels revealed by Western analyses of total microsomes prepared from tobacco leaves transfected with ABCB1 (upper panel). Microsomes were stained for GFP and plasma membrane marker, PIP2;1. ABCB1 expression was evaluated by calculating GFP/PIP ratios from three independent tobacco transfections (lower panel). C and D, IAA (C) and BA (D) export of protoplasts prepared from tobacco leaves transfected with WT and indicated proline mutants of ABCB1. E, vanadate (Vd)-sensitive ATPase activity of microsomal fractions prepared from tobacco leaves transfected with WT and indicated proline mutants of ABCB1; controls are in Fig. S6. Significant differences (unpaired t test with Welch's correction, p < 0.05) to vector control or ABCB1 are indicated by an “a” or a “b,” respectively. Mean ± S.E.; n ≥ 4 transport experiments generated from independent tobacco transfections.