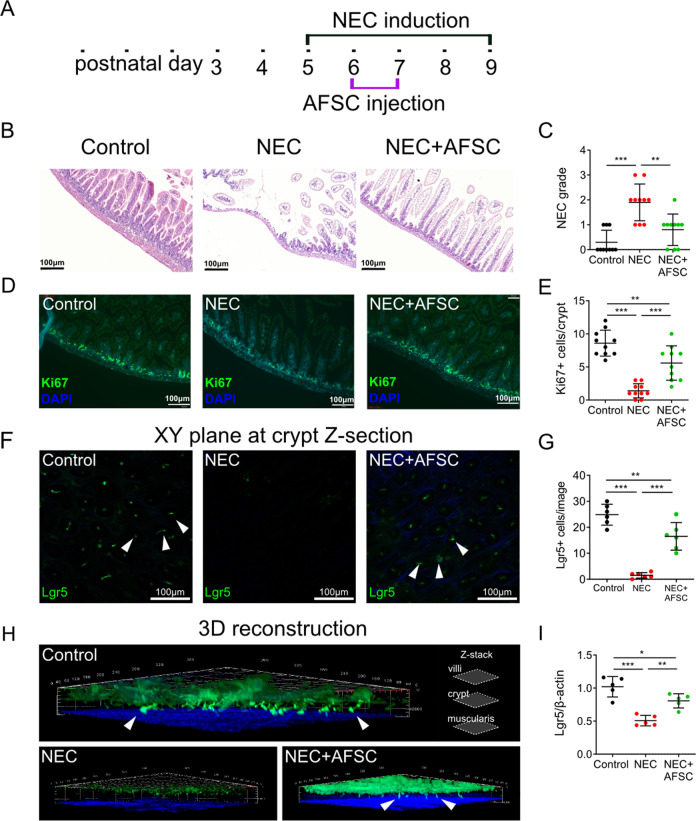
Fig. 1. Amniotic fluid stem cells (AFSC) rescued intestinal injury, restored epithelial regeneration, and increased active intestinal stem cells (ISC).
NEC induction was conducted on postnatal (p) days 5–9, with AFSC intraperitoneal injections given on p6 and p7 (a). Histopathology of ileal sections from mice administered with AFSC during necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) induction showed normal villous structure when compared to NEC mice (b). Administration of AFSC during NEC significantly decreased histological scores (c). Intestinal epithelial proliferation (Ki67), which is reduced in NEC, was restored with AFSC administration (d, e). In vivo visualization of ISC after NEC induction showed a decrease in Lgr5+ ISC, some of which are denoted with white arrows, expression in NEC and restoration after AFSC treatment (f–i). n = 10 for each group (b–e) and n = 6 for each group (f–i). Data are presented as means ± SD. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001, using unpaired Student’s t test or one-way ANOVA with post-hoc tests as appropriate.