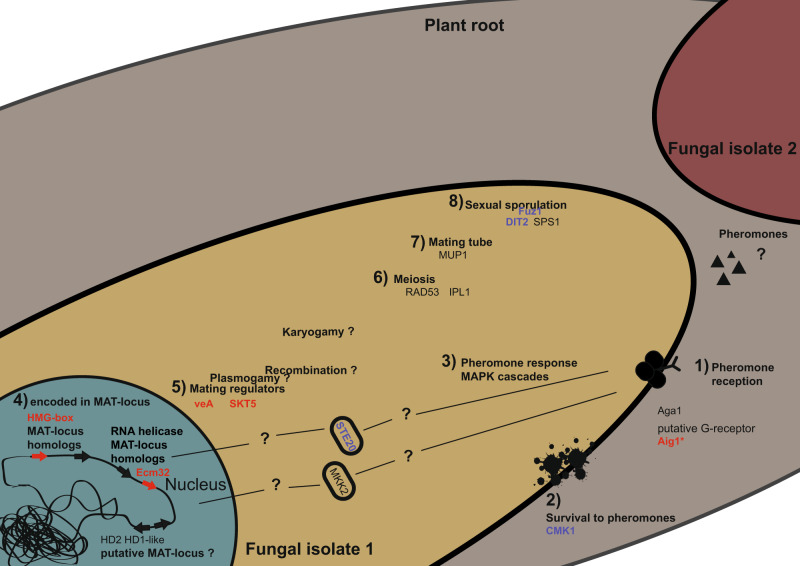
Fig. 4. Schematic representation of the putative mating response in R. irregularis.
We identified homologs of genes involved in (1) pheromone reception, (2) survival to pheromones, (3) different pheromone response MAPK cascades, (4) encoded in MAT-locus, (5) mating regulation, (6) meiosis, (7) formation of the mating tube, and (8) sexual sporulation. We did not observe upregulation of homeodomains proposed on a putative R. irregularis MAT-locus. We did not find upregulation of genes encoding the mating pheromones or those involved in plasmogamy, karyogamy, and recombination. Genes in blue were observed in host plant genotypes COL2215 and CM4574. Genes in red were observed in the three host plant genotypes in the coinoculation treatment specifically.