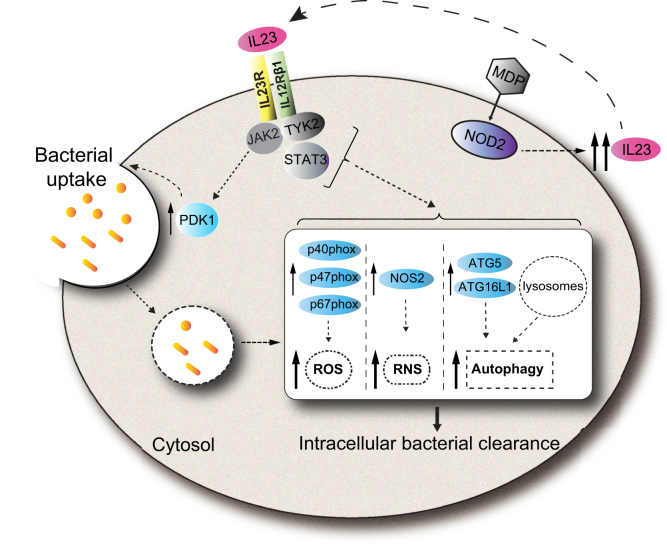
Figure 19.
Model of IL23 contributions to antimicrobial pathways in human macrophages. IL23 treatment of human macrophages activates the PDK1 pathway, which leads to bacterial uptake, and the JAK2, TYK2, and STAT3 pathways, which lead to enhanced clearance of intracellular bacteria through induction and cooperation of ROS (NADPH oxidase subunits), RNS (NOS2), and autophagy (ATG5 and ATG16L1) pathways. Upon PRR stimulation, autocrine/paracrine IL23 promotes each of the IL23-dependent antimicrobial pathways identified. Compared with IL23R–R381/R381 carriers, MDMs from IBD-protective IL23R–R381/Q381 carriers show a reduced ability to induce each of these antimicrobial mechanisms. MDP, muramyl dipeptide.