Figure 6.
Examples of MAPs Whose Structure Has Been Determined as a Complex with Microtubules but Not with Tubulin
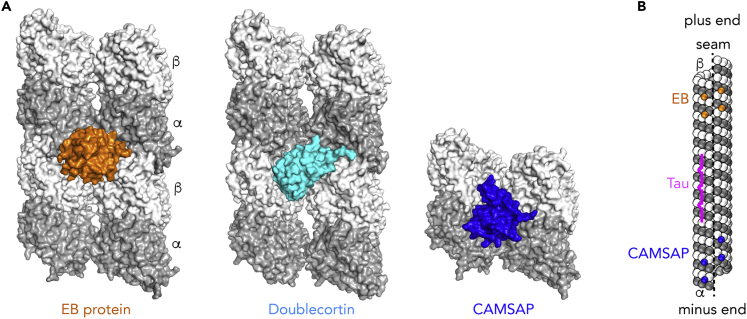
(A) Proteins that bind at the inter-protofilament interface. EB proteins (Maurer et al., 2012; Zhang et al., 2015) and doublecortin (Fourniol et al., 2010) bind at the corner of four tubulin heterodimers, whereas the CKK domain of CAMSAP proteins (Atherton et al., 2017a) targets two adjacent tubulin molecules.
(B) Schematic drawing of a 13-protofilament microtubule. EBs bind preferentially to the growing ends of microtubules (shown here at the plus end), whereas CAMSAP targets and stabilizes the minus end. The binding mode of these proteins implies that they do not target the microtubule seam (dashed line), where interactions between adjacent protofilaments are heterotypic (α-tubulin interacting with β-tubulin and vice versa). Because they bind at the corner of four tubulin subunits, these proteins can modulate both longitudinal and lateral interactions. In contrast, the microtubule-binding repeats of Tau (magenta) bind at the crest of one protofilament, with a major effect on longitudinal contact stabilization.