Figure 2.
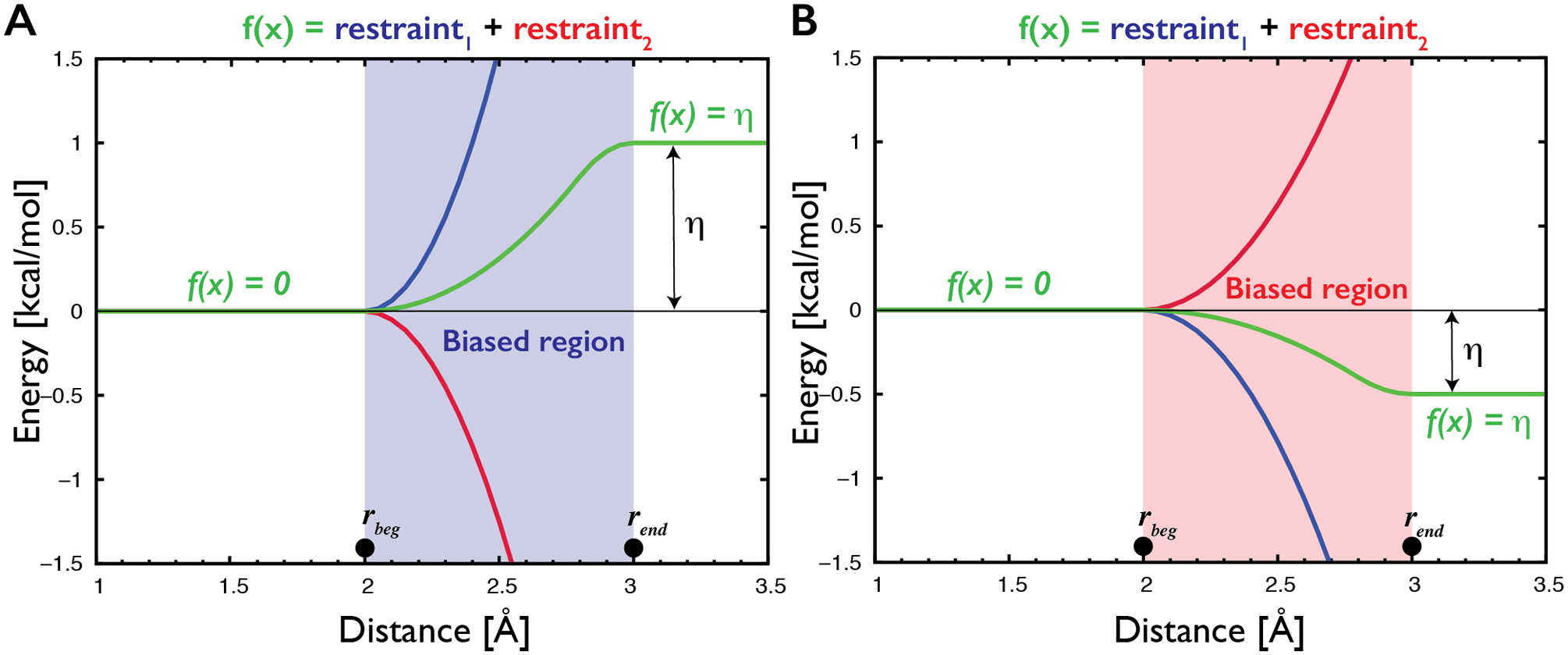
Description of the gHBfix potential (green curves) used for either support (A) or weakening (B) of H-bond interactions. In the present study, gHBfix potential is in all cases applied to the distance between hydrogen of the proton donor and proton acceptor heavy atom. The potential is constant (i.e., it provides zero forces) at all distances except for the narrow region between rbeg and rend corresponding roughly to the expected location of the free energy barrier between bound and unbound states. For the used distance between hydrogen and proton acceptor heavy atom of the hydrogen bond we applied here 2 Å and 3 Å for rbeg and rend, respectively. The potential is formally composed of a combination of two flat-well restraints with opposite sign of curvature and linear extensions that cancel each other at distances above rend (red and blue curves). The η parameter defines total energy support (A) or penalty (B) for each H-bond interaction. Although the gHBfix potential is technically constructed using two restraining functions, it is not a restraint; we have used this technical solution solely in order to be able to efficiently use common functions that are available in the simulation codes without any necessity to modify them.
