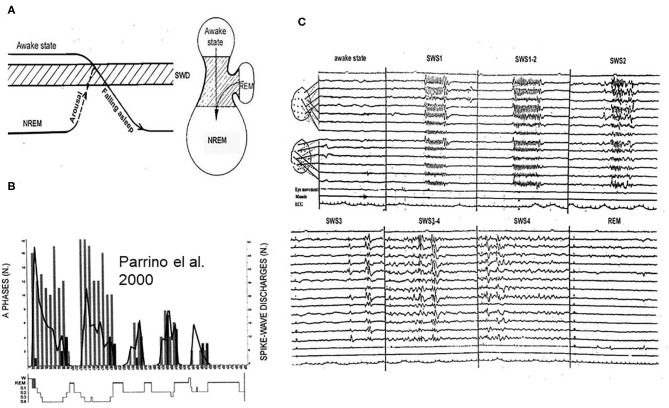
Figure 4.
(A) The vigilance dependence of absences. Left: Arriving to the critical vigilance state (hatches) from awake sate or from deeper sleep, AE prone patients display absences. Right: the jar- like formation represents the states of existence: lower part: NREM sleep, upper part: awake state, and handle of the jar is REM sleep. The critical zone for absences is in-between. (B) Night sleep of a typical absence patient. The perpendicular columns represent cyclic alternating pattern (CAP) A1 phases (phasic slow waves), the graph shows the number of spike-wake seizures: decreasing from evening to morning. (C) The distribution of absences across the sleep cycles. During slow wave sleep phase 1 (SWS1) and phase 2 (SWS2) synchronized spike-wave runs (absences) occur, during SWS3 spike wave paroxysms cease, scattered IEDs display (mainly individual spike-waves). During REM sleep, there is no spike wave discharge.